- November 28, 2025
- 19 min read
Mirror Trading: How to Trade Like the Pros
Have you ever wondered how you could take part in the financial markets without spending years learning trading, analysing charts, executing trades, or dealing with the constant pressure of market fluctuations? One way traders do this is through an innovative approach known as mirror trading.
Mirror trading allows you to replicate predefined, algorithmic strategies automatically in your account, removing the need for constant manual analysis and execution.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the concept of mirror trading, and how this automated tool can help simplify your trading journey.
What is Mirror Trading?
Mirror trading first emerged in the early 2000s when institutional traders began using it to replicate algorithmic strategies. At first, it was mainly a tool for hedge funds and professional investors, but as online trading platforms grew, it became available to the wider public around 2005–2010.
Mirror trading is a method that allows users to automatically replicate predefined, algorithmic strategies uploaded by professional traders. Instead of manually analysing charts and placing orders, the system executes trades based on those rule-based strategies. This ensures consistent execution and removes the influence of human discretion or emotions. Essentially, mirror trading provides access to tested strategies without requiring constant supervision or deep market knowledge.
This approach is especially appealing to users who do not have the time or expertise to monitor markets. By selecting an algorithmic strategy created by a professional trader, you gain access to a predefined, rule-based system that executes trades automatically. Essentially, the algorithm handles the heavy lifting while you focus on your overall investment goals.
How Does Mirror Trading Work?
Mirror trading works by automatically replicating every action of a selected algorithm with a predefined strategy in your account in real time. When it generates a buy or sell order, adjusts a stop-loss, or closes a position, the same action happens in your account.
Mirror trading allows you to closely copy an algo’s:
- Entry price levels
- Stop-loss placements
- Take-profit targets
- Direction of the trade (buy or sell)
- Assets traded, such as forex pairs, stocks, indices, or cryptocurrencies
- Risk management strategy, for example risking 0.5 to 1 percent of the account per trade
Lot sizes are usually adjusted to your account balance. For example, if an algorithm is designed for a $100,000 account and opens a 1-lot position, and you have a $10,000 account, the system might open a 0.1-lot position for you, keeping the risk proportional.
This proportional scaling ensures smaller accounts do not take on excessive risk while still applying the same predefined rules. Users can also adjust capital allocation or stop running an algorithm at any time, so you remain in control of your account.
The beauty of mirror trading lies in its simplicity. Trades are executed rapidly and precisely, giving users access to tested algorithms with predefined strategies without the need for constant analysis or manual execution.
Mirror Trading Strategies
Mirror trading provides access to a variety of trading strategies that can be applied across different markets and conditions. These strategies range from long-term approaches designed for steady growth to short-term methods that seek to capture quick market movements.
Each one has its own characteristics, advantages, and risks, allowing users to see how different styles of trading can be mirrored automatically within their own accounts:
Trend-Following Bots Strategy
Trend-following is one of the most common approaches in mirror trading. The idea is simple: when markets are trending upwards, algorithms look for rules that signal buying, and when they trend downwards, they look for signals to sell.
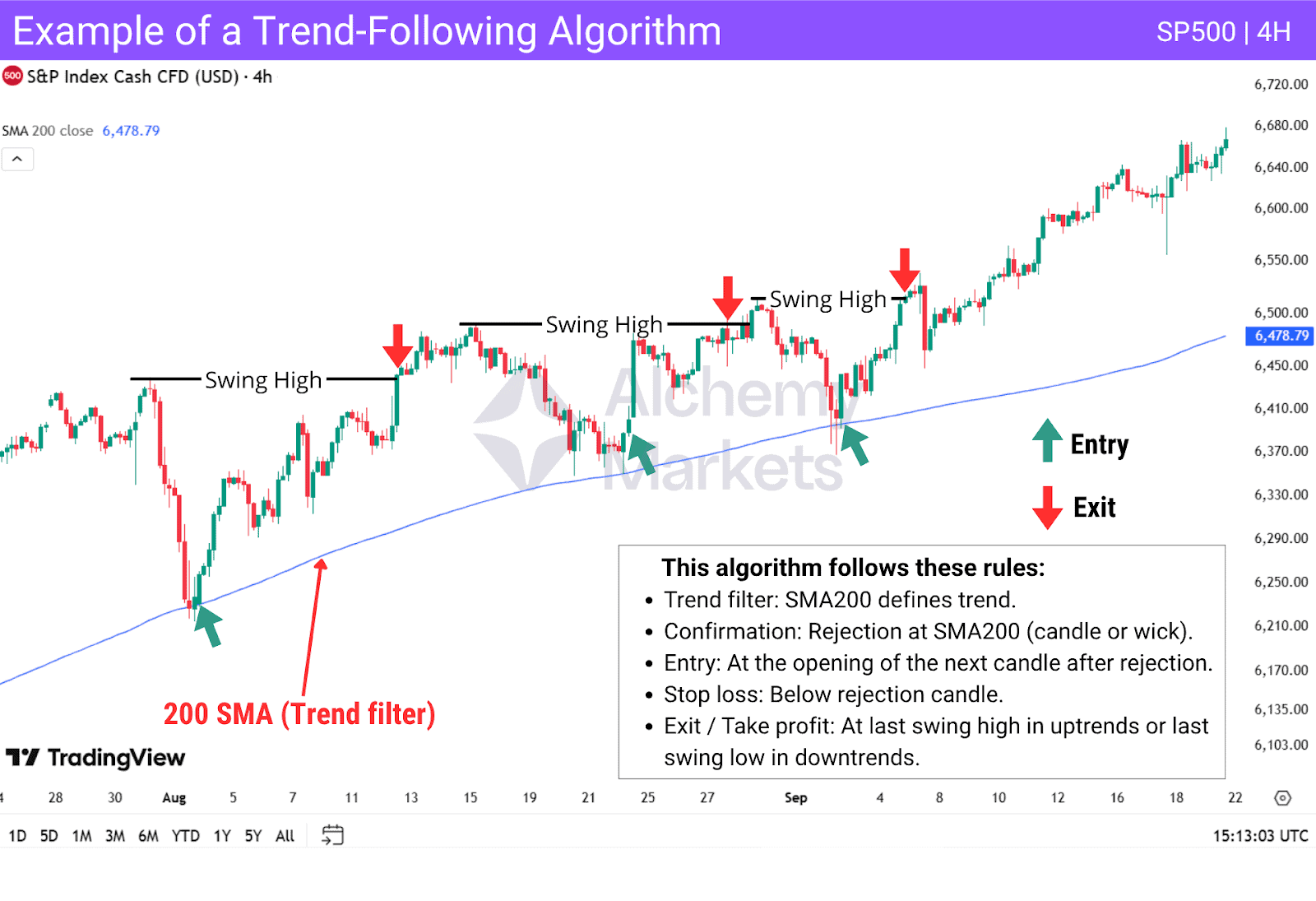
Trend-following algorithms can be designed in different ways, but most follow three general steps:
- Identify the trend – Algorithms may use tools such as trendlines, moving averages (e.g., SMA200), market structure (higher highs/lows in uptrends, lower lows/highs in downtrends), or trend indicators like SuperTrend or the Trend Exhaustion Indicator.
- Confirm entries – Rules can include conditions such as volume thresholds, candlestick patterns, or rejections at certain levels (e.g., discount zones after a pullback). Once those conditions are met, the algorithm enters on the next candle.
- Set exits – Exit rules vary but must also be rule-based. Algorithms may:
- Use indicators such as RSI or the Stochastic Oscillator, or any indicator capable of identifying overbought and oversold bands to signal trade exits.
- Set predefined targets at recent highs/lows.
- Employ trailing stops, where the stop-loss moves up each time price reaches a new level, protecting profits while allowing trades to run.
- Use indicators such as RSI or the Stochastic Oscillator, or any indicator capable of identifying overbought and oversold bands to signal trade exits.
Main Takeaway: Trend-following algorithms rely on absolute, coded rules to trade consistently with market direction. While they can perform well in trending conditions, they often face challenges in sideways or highly volatile markets where signals become less reliable.
Scalping Bots Strategy
In mirror trading, scalping is carried out by scalp bots that mirror accounts and place numerous trades on very short timeframes. The goal is not to capture large swings but to take advantage of small price fluctuations, stacking many modest gains throughout the day.
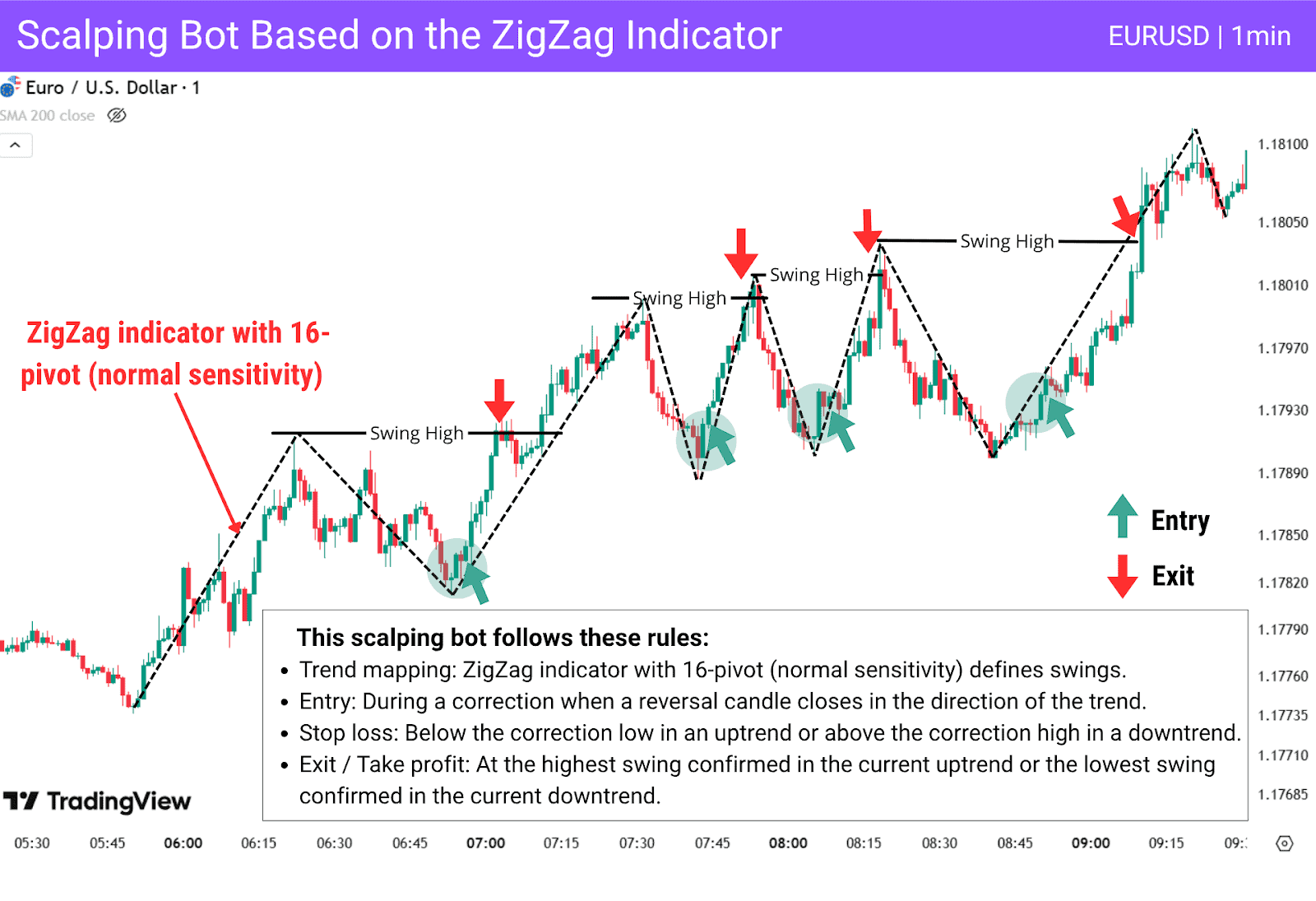
Here’s how scalping bots typically operate:
- Identify setups – Bots monitor short-term market movements to detect quick opportunities.
They may:- Spot breakouts when price pushes above a recent high.
- Detect mean reversion setups when price spikes and then reverts toward an average.
- Track momentum surges through volume spikes or candlestick signals.
- Refine short-term swings using ZigZag or similar tools.
- Confirm entries – To reduce false signals, bots apply filters and indicators, such as:
- RSI for overbought/oversold conditions.
- Volume to confirm strength behind a move.
- Candlestick patterns to validate price behaviour.
- Set exits – Scalping bots code risk and profit rules directly into the system:
- Tight stop-losses to limit downside on quick reversals.
- Small lot sizes to manage exposure.
- Modest, predefined profit targets to lock in gains.
Main Takeaway: Scalping bots perform best in highly liquid markets such as forex, where fast execution and low spreads support frequent trades. This frequency of trades may look attractive, as it creates many opportunities, but you should also consider the costs of trading. Spreads and commissions can eat into the small profit margins that scalping relies on, so it is better to use an account with low spreads and minimal commission to align more effectively with this strategy.
Range-Bound Bots Approach
The range-bound strategy seeks to profit when markets move sideways, with price oscillating between clear support and resistance levels rather than trending in one direction. Traders (or algorithms) anticipate that price will continue rebounding within these boundaries until a breakout occurs.
How It Works:
- Identify setups – Bots scan for consolidation phases by combining price structure with volatility tools such as the Average Directional Index (ADX) or the Average True Range (ATR). Support and resistance zones, pivot points, equal highs/lows, and periods of low trading volume also help confirm range conditions.
- Confirm entries – Once the range is clear, bots validate setups with technical signals, such as:
- RSI or Stochastic Oscillator showing overbought/oversold conditions.
- Candlestick reversal patterns at support or resistance.
- Some models also use Bollinger Bands or moving averages for added confirmation.
- Set exits – Rules are pre-coded for consistency:
- Longs close as RSI or Stochastic approach overbought levels.
- Shorts close as RSI or Stochastic approach oversold levels.
- Alternatively, bots may target the opposite range boundary or exit on stop-losses just outside the range.
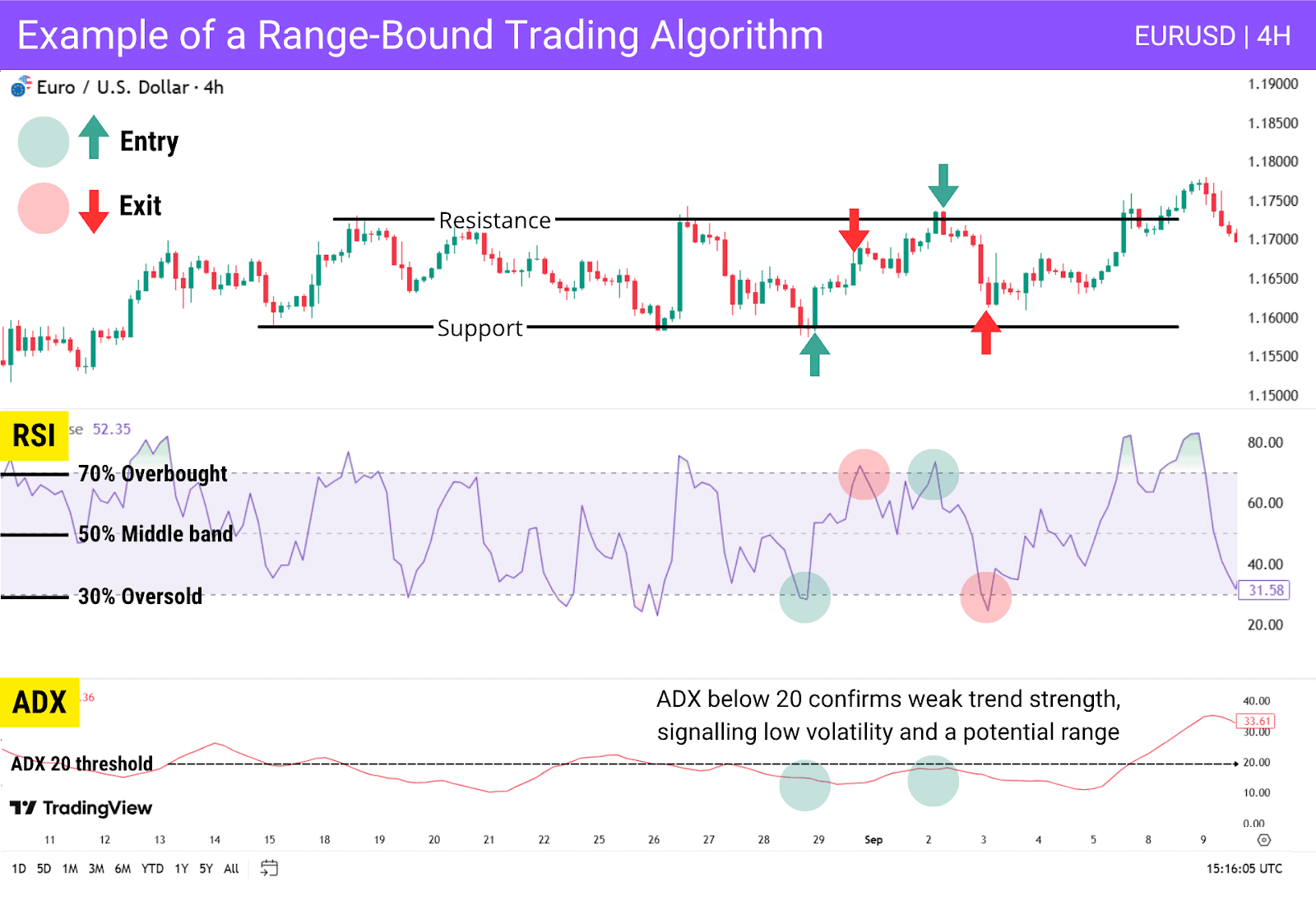
This example represents a range-bound trading algorithm on the EUR/USD 4H chart. The system uses support and resistance, RSI, and the ADX to identify ranges and trading opportunities within them. Equal highs form resistance while equal lows mark support.
A long is triggered when price tests support while RSI rebounds from 30; a short when price tests resistance while RSI turns down from 70. Exits follow the opposite RSI levels, keeping execution systematic.
Main Takeaway: Range-bound mirror trading works best during low-volatility range periods. Its effectiveness decreases when markets transition into trending phases and when breakouts occur.
Algorithm-Based Strategies
All mirror trading is technically algorithm-based since it relies on predefined rules coded into systems that open and close trades automatically. Traders design these mechanical strategies using technical indicators, price action, fundamentals, or other rule-based setups.
Once programmed, the algorithm executes trades whenever its conditions are met, ensuring consistency and eliminating emotional decision-making.
What differs is the type of strategy the algorithm follows, whether it is trend-following, scalping, range-bound, or a hybrid that adapts to changing market conditions. These algorithms are copied directly into follower accounts, executing trades without manual input.
Main Takeaway:
- Algorithms bring consistency and speed, can be backtested for accuracy, and scaled across multiple markets and timeframes.
- Their main limitations are that only mechanical rules can be coded and they often struggle when market conditions shift, requiring monitoring and optimisation.
- They are most effective for traders who want emotion-free systems in stable markets and can serve as the umbrella layer for strategies such as trend, range, or scalping bots.
Mirror Trading via Crypto Platforms
Crypto mirror trading bots are unique because they can use blockchain-native data rather than just price and volume. This includes signals like funding rates, open interest, order flow, and even ETF flows.
How It Works:
Bots scan crypto markets for conditions that reveal imbalance or momentum:
- Funding rates in perpetual futures indicate when longs or shorts are overcrowded, often warning of a possible reversal.
- Open interest tracks trader participation. Rising OI with price supports a stronger trend, while falling OI suggests weakening conviction.
- Order-flow and liquidity shifts show pressure in real time, with large buy or sell walls hinting at temporary barriers, though bots must filter for spoofing.
- ETF flows can sometimes alter demand, especially in Bitcoin and Ethereum, and are factored into certain models.
Main Takeaway: Mirror trading in crypto is distinct because it blends on-chain data with traditional technical signals, giving systematic exposure to digital assets. However, crypto’s volatility, thin liquidity, and shifting market structure demand frequent optimisation and careful risk management to keep strategies effective.
Shell Firm Mirror Trading
The term “mirror trading” isn’t always about algorithms. Regulators also use it to describe schemes where trades are routed through shell companies — firms that exist mostly on paper.
One of the most infamous examples was the Deutsche Bank scandal (2011–2015), where billions were funnelled out of Russia through mirror trades. Cases like this show how the same phrase can mean money-laundering practices that have nothing to do with legitimate trading strategies.
Main Takeaway: Shell firm mirror trading is not a legitimate trading approach but a regulatory red flag, often linked to money-laundering schemes. Retail traders should ignore this usage entirely and focus only on regulated platforms that offer transparent, rule-based strategies.
How to Copy Trading Strategies of Experienced Traders
Successful mirror trading starts with preparation. To use it effectively while keeping risk under control, you need clear objectives, careful strategy selection, and disciplined evaluation of performance metrics.
How to Evaluate a Trader
Before mirroring a trader’s strategy, assess their performance carefully. Review key metrics such as win rate, average trade duration, drawdown, and number of trades to gauge consistency and risk level.
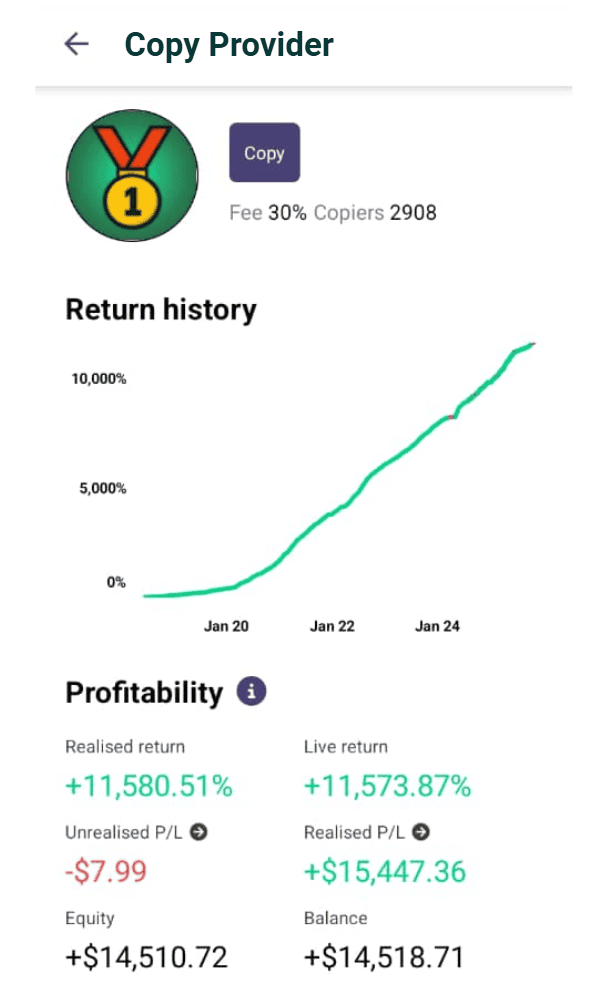
A trader with steady returns and controlled drawdowns is generally a safer choice than one who relies on a few large wins. Always check the track record length and transparency of results before mirroring.
Selection of Traders
Start by choosing traders or strategies that align with your objectives and risk tolerance. The most reliable way to do this is by reviewing measurable statistics. The table below highlights the most important metrics to consider, with explanations and examples:
| Metric | Explanation | Consideration |
| Equity Curve | Visual record of account growth over time, showing stability or volatility. | A steady upward slope is more consistent than sharp spikes and crashes. |
| Number of Trades | Total trades taken, which impacts statistical reliability. | Prefer 200+ trades and at least 12 months of live results. |
| Maximum Drawdown (MDD) | Largest account decline from peak to trough before recovery. | A 25% drawdown means $10,000 dropped to $7,500 at its lowest point. |
| Profit Factor | Ratio of total profit to total loss. | A profit factor above 1.5 is generally considered strong. |
| Trading Style | Defines the approach used by the strategy (trend-following, range, scalping, etc.). | Make sure the style aligns with your objectives and risk tolerance. |
| Fund Allocation | Percentage of your total capital assigned to each trading strategy. | Allocating 20% of your account means all trades from that strategy are scaled to 20% of your balance. |
Always favour strategies where the trader or system is transparent about their method and risk management. Past performance can provide useful insight but will vary depending on market conditions.
For example, mean-reversion systems may perform best in sideways markets but struggle during strong trends.
Automation
Once you select a trader or strategy, the platform mirrors their trades automatically in your account. You control the capital allocation and can set overall risk limits, such as maximum exposure or daily loss caps. This ensures the strategy runs at a scale that fits your portfolio, without requiring constant monitoring.
Technology Integration
Mirror trading runs directly on the broker’s servers. Once you follow a trading strategy, all of its trades are copied to your account automatically, 24/7, even if you are not logged in. Reliable platforms also provide tools for monitoring performance, setting allocation, and managing overall risk.
Advantages of Mirror Trading
Mirror trading provides retail traders with access to professional strategies in a fully automated way. It helps save time, diversify portfolios, and potentially enhance returns.
| Advantage | Description |
| Accessibility | Mirror trading makes predefined algorithmic strategies accessible to users of all levels, even those without prior trading experience. |
| Time-Saving | Automation allows for hands-off trading, eliminating the need to monitor markets and place trades manually. |
| Diversification | By following multiple providers with different strategies, you can spread your risk across various markets, reducing the impact of a single loss. |
| Potential Passive Returns | For many investors, mirror trading creates a potential stream of passive income, allowing them to participate in forex and stock markets without constant trading decisions themselves. |
Disadvantages of Mirror Trading
Despite its benefits, mirror trading carries risks linked to dependency on traders and algorithms. Poor performance or market shifts can still result in losses.
| Disadvantage | Description |
| Dependency on providers | Your success depends on the algorithm’s performance and market conditions; if they shift unfavourably, the strategy may generate losses that will also affect your account. |
| Potential Losses | While it offers convenience, mirror trading doesn’t eliminate risk. Weak or poorly coded strategies can lead to significant losses, especially if they are not updated to adapt to changing market conditions. |
| Over-Reliance on Automation | Over-reliance on automated systems can reduce personal involvement, which might prevent you from learning and adapting to market changes. |
Choosing the Right Mirror Trading Platform
Selecting the right platform is key to your success in mirror trading. A reliable platform should provide an intuitive interface, transparent fee structures, and robust security features to protect your investments.
Additionally, the platform should be regulated by trusted financial authorities, ensuring safety and fairness in your trades. Here are key factors to consider when choosing a mirror trading platform:
- User-Friendliness: Ensure the platform is easy to navigate, even for beginners.
- Fees: Check for clear, upfront fees, including performance and transaction costs.
- Regulatory Standards: Choose platforms regulated by trusted authorities for added security.
- Real-Time Data: Ensure the platform offers live market data and updates.
- Risk Management Tools: Look for adjustable stop-loss features and risk controls.
- Customer Support: Accessible support to assist with technical or account-related queries.
Looking to get started?
Become a copier or provider in minutes with Alchemy Markets Copy Trading.
Risk & Regulationary Concerns
Mirror trading is a legitimate strategy on regulated platforms, but it has also been misused by bad actors. Fraudulent schemes such as Mirror Trading International (MTI) show how unregulated platforms can exploit the term mirror trading to gain investor trust.
MTI claimed to use a “mirror trading bot” to generate steady Bitcoin profits, yet no trading ever took place. The platform was later exposed as one of the largest crypto Ponzi schemes in history.
Cases like this underline the importance of verifying a provider’s credibility before connecting your account or depositing funds.
To stay protected, trade only with regulated brokers. Regulation ensures transparency, client fund protection, and fair execution — all essential safeguards in any automated or replicated trading system.
Regulatory Oversight
Since mirror trading involves third-party trade replication, it’s essential to use platforms regulated by trusted authorities such as the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) or the Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC) to protect investor funds.
Alchemy Markets operates under dual regulation, authorised by the Financial Services Authority (FSA) in Seychelles and the Malta Financial Services Authority (MFSA). This oversight provides traders with extra protection and ensures compliance with international standards.
Automated Trading vs Social Trading vs Mirror Trading
Each trading approach offers a different balance between automation, human decision-making, and control. Understanding how they differ helps traders choose the method that best fits their goals and level of involvement.
| Approach | How It Works |
| Automated Trading | Uses pre-programmed algorithms or bots to execute trades automatically based on predefined rules and conditions. |
| Social Trading | Lets users follow and manually copy trades or ideas shared by other traders within a community. |
| Mirror Trading | Automatically replicates the exact trades of a selected algorithm in real time, often on a performance-fee model. |
Mirror Trading vs Social Trading
Social trading revolves around sharing ideas, insights, and trade signals within a community (think chatgroups where signals are shared). Traders can choose which positions to copy, but the process is still manual or semi-automatic, depending on the platform. It’s often used as a learning tool, allowing beginners to follow experienced traders while keeping full control over execution.
Mirror trading, on the other hand, is fully automated. Once you select a trading bot to mirror, every trade is replicated in your account in real time. This removes hesitation and emotion from decision-making, but it also means you rely entirely on the mirror provider’s strategy and performance.
Mirror Trading vs Automated Trading
Automated trading, also known as algorithmic trading, uses pre-programmed bots to execute trades based on fixed rules. These bots automatically open and close positions when their entry and exit conditions are met, removing much of the time and emotional strain of manual trading.
Mirror trading takes this concept a step further by allowing traders to copy an algorithm’s strategy directly, provided the creator makes it available for mirroring. This differs from running your own bot. In most mirror trading setups, users pay a small performance fee only when profits are made — a “pay-as-you-earn” model.
By contrast, traders who own or subscribe to algorithms outright typically pay a one-time purchase or monthly subscription fee, regardless of performance. Mirroring allows investors to participate in algorithmic systems without owning the code or managing the bot themselves, making it a more accessible, performance-based approach.
Mirror Trading vs Copy Trading
While mirror trading and copy trading may seem similar, they differ in key ways. Mirror trading involves fully replicating the entire portfolio of a trader, including every position and strategy, while copy trading generally focuses on copying specific trades or strategies.
In practice though, most modern copy trading apps also cover mirror trading. Users can often choose to copy not just human traders, but also algorithmic strategies to diversify their approach.
| Mirror Trading | Copy Trading |
| Replicates an entire trading strategy automatically, including all signals generated by algorithms. | Copies individual trades from a trader’s account in real time. |
| Strategy is rule-based and backtested, focused on consistent execution. | Driven by the discretion and decision-making of human traders. |
| Works best for traders seeking a fully automated and systematic approach. | Offers flexibility to choose multiple traders and diversify strategies. |
FAQs
What is the origin of Mirror Trading?
Mirror trading originated as a way to replicate algorithmic strategies created and coded by professional traders. It became popular in the early 2000s with the growth of online trading platforms.
How reliable is Mirror Trading?
Mirror trading can be reliable if you select well-tested algorithmic strategies with proven performance records, but, like any form of trading, it still involves risk and market unpredictability.
Is Mirror Trading Suitable for Beginners?
Yes, mirror trading is an excellent option for beginners as it allows them to copy predefined algorithmic strategies without needing deep market knowledge.
Can I Lose Money with Mirror Trading?
Yes, mirror trading does not eliminate risk. If the trader you’re copying suffers losses, your account may also reflect those losses.
How do I Know if a Trader is Worth Following?
Look for traders with consistent performance, transparency, and a solid risk management strategy. Platforms often provide performance metrics to help with this evaluation.
What Common Mistakes Should Traders Avoid When Using Mirror Trading?
Traders should avoid blindly following a trader without understanding their strategy or risk levels. It’s also important not to place all funds in a single trader’s hands.
What’s the Minimum Amount Needed to Start Mirror Trading?
The minimum amount varies by platform, with some starting from as low as $0. Always check the platform’s requirements before committing.
How Do Mirror Trading Fees Impact Returns?
Mirror trading platforms may charge performance fees, spread costs, or other transaction fees. These fees can reduce your overall returns, so it’s essential to consider them when choosing a platform.
Is mirror trading worth it?
Mirror trading can be worthwhile for investors who prefer a hands-off, rules-based approach to the markets. It offers access to professional-level strategies without requiring constant monitoring or advanced technical knowledge. Success depends on the trader you mirror and the transparency of the platform you use.
Is mirror trading illegal?
Mirror trading itself is legal when done through regulated brokers. It only becomes problematic when used in unregulated or fraudulent setups, such as the Mirror Trading International (MTI) scam, which misused the term to lure investors.
Always ensure your trading provider is regulated by authorities such as the FSA, MFSA, FCA, or CySEC for full investor protection.