
- February 14, 2025
- 26 min read
Gold CFDs – Buy, Sell and Trade
Gold CFDs help traders gain exposure to the precious metal without having to buy it physically, which is more convenient for active trading. In this article, you’ll learn how gold CFDs work and how you can trade them.
What Are Gold CFDs?
Gold CFDs (short for contracts for difference) are a type of derivative that gives investors exposure to gold’s price movements without having to own the yellow metal. Trading CFDs, especially in the context of engaging with financial markets, allows investors to trade gold through brokerage platforms.
The goal of any CFD is to mirror the price movement of the underlying asset, allowing traders to take short-term or medium-term positions in an effort to profit from either the asset’s price rise or fall.
Other derivatives, such as futures and options, can also provide indirect exposure to gold, but CFDs are more flexible, straightforward, and optimised for active trading.
One can trade gold CFDs through brokerage firms. Most of them offer more than metals and commodity CFDs but also support a wide range of asset classes, including foreign exchange (forex) pairs, equities (stocks), and cryptocurrencies. This allows traders to build diversified portfolios by mixing assets that show lower correlations with each other.
How Do Gold CFDs Work?
A Gold CFD is an agreement between a trader and a broker, where the trader is paid the price difference from the time the position is opened to when it is closed, provided they accurately predict the price direction. Conversely, if the price moves in the opposite direction, the trader incurs a loss, which is deducted from their balance. Therefore, trading gold CFDs is essentially a financial bet on the price direction of the metal.
Traders can buy or sell gold CFDs. Buying the CFD will result in a profit if the trader closes the position above the entry price (the green zone in the image below). In trading jargon, buying is also referred to as ‘go long’ or ‘opening a long position’.
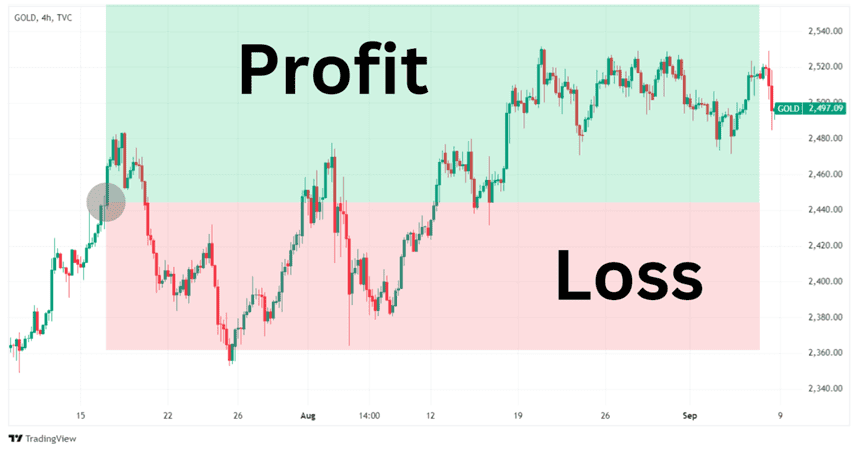
Example: Hypothetical chart of a trader opening a long position in a Gold CFD.
Selling a gold CFD will result in a profit if the trader closes the position below the entry price. Selling a CFD is also referred to as ‘open a short position’ or ‘going short.’
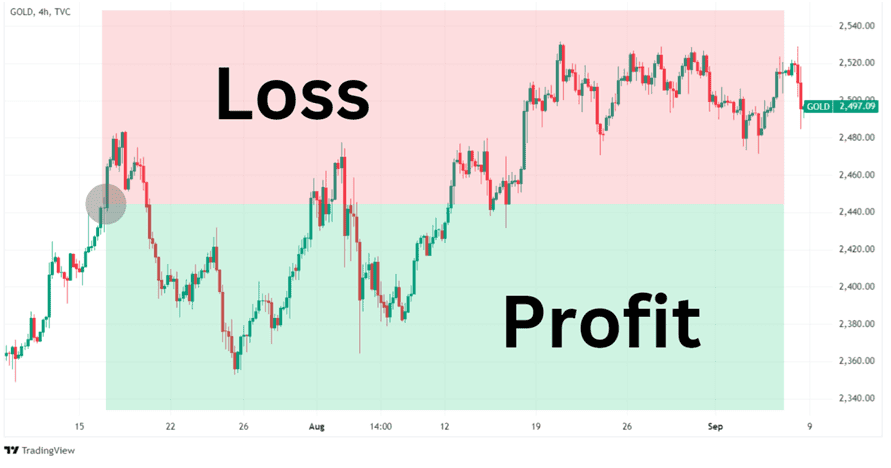
Example: Hypothetical chart of a trader opening a short position in a Gold CFD.
The size of the profit or loss depends on how much the exit price has moved from the entry price, reflecting the price changes during the open position.
Traders can multiply their trade’s outcome, whether it is a profit or loss, by using margin. This feels great when the trade works out in your favor as a profit. However, trading on margin can be devastating if the market moves against your position as losses will pile up quickly.
Trading CFDs on margin is borrowing funds from the broker to increase the position size. So, you are essentially opening a position size larger than the cash deposit required to open the trade. Using margin amplifies the trade’s profit or loss, offering the potential for amplified earnings but also heightened risks. If the losses are great enough, the broker will automatically close the position if the trader’s available margin runs out and they can no longer cover pending losses.
What’s the Symbol of Gold CFD?
If you’ve ever traded forex pairs, you’d realise that trading gold CFDs is quite the same. Instead of dealing with pairs like EUR/USD, you should look for gold’s trading code, which is XAU.
‘X’ in XAU is a code for commodities and several non-national currencies, while ‘AU’ is from Aurum – gold’s name in Latin.
The most popular gold CFD product is XAU/USD, which represents the USD price per troy ounce. Some brokers, like Alchemy Markets, support other gold denominations such as XAU/EUR. This means gold is priced in Euros and the value of the contract fluctuates as the Euro moves up and down.
Key Elements of a Gold CFD
A gold CFD comprises several basic attributes that are valid for any CFD:
- Ask price, which is the price at which traders are able to purchase the gold CFD.
- Bid price, which is the price at which traders are able to sell the CFD.
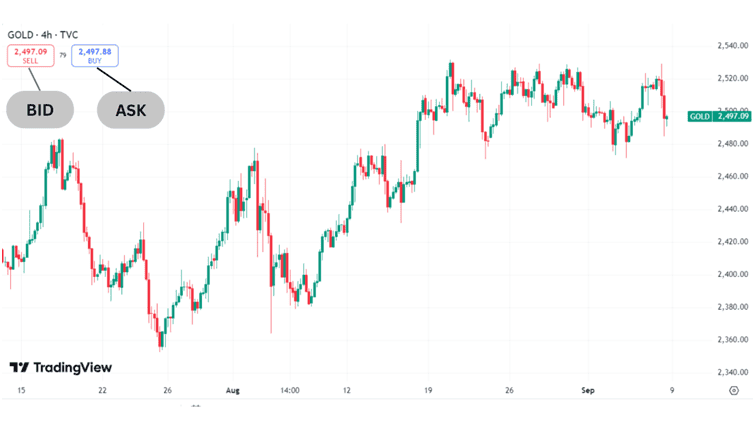
- Spread, which is the difference between the bid and ask price, represents a hidden cost of the trade. The spread takes effect once a position is opened.
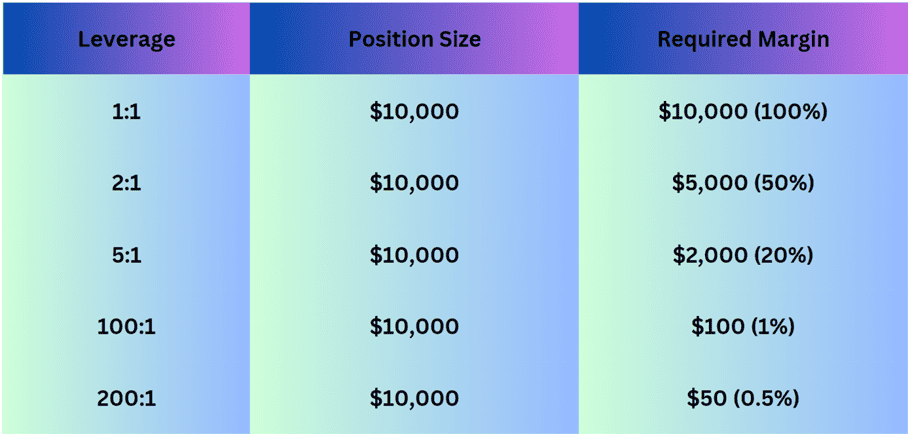
- Leverage is a ratio showing how much margin a broker would require to open a position. The margin is a good faith deposit the broker uses to hold the position open. Any profits or losses are added and subtracted to the unused or available margin so it is important that traders manage their available margin to keep a cushion to withstand future losses.
With leverage, a trade with 5:1 leverage would require a 20% margin, and that would require the trader to commit $200 as a good faith deposit to open a $1,000 position.
Check this table to see the margin requirements for the main leverage scenarios:
Physical Trade in Gold
CFDs offer exposure to the gold price but don’t provide ownership of the metal.
Investors may choose to buy physical gold directly. They can buy gold bars and coins from bullion dealers or opt for gold jewellery, although the latter may involve additional costs for design and craftsmanship. When buying jewellery or other forms of physical gold, you should check its purity, which is measured in karats. Check this table to decode gold quality based on its karat rating:
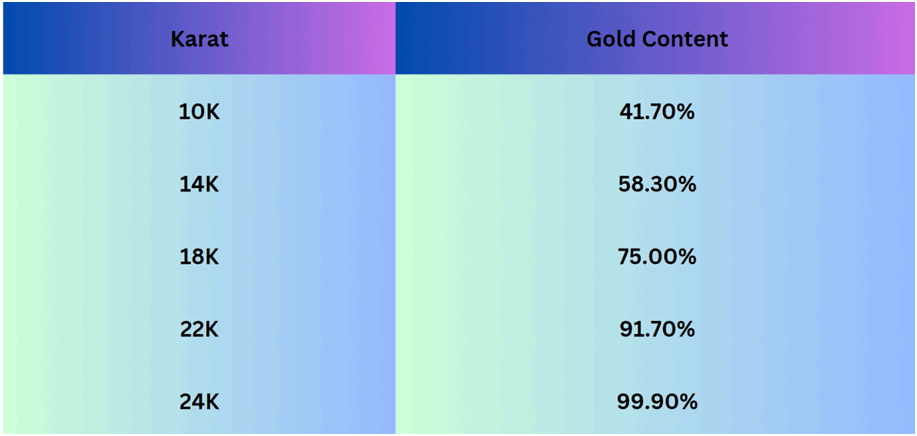
Buying physical gold would require secure storage as well.
Another way to get more direct exposure to the yellow metal is through gold exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that hold physical gold in their reserves.
What Affects the Price of Gold CFDs?
The price of a gold CFD is directly affected by the gold price since the derivative mimics the metal price based on a 1:1 ratio. Therefore, let’s explore the main factors affecting gold’s value:
Gold Supply and Demand
Like any asset, the dynamics of supply and demand significantly impact the price of gold. Generally, higher demand drives prices up, while an increase in supply tends to put downward pressure on them.
Gold is one of the scarcest metals and assets, and its production doesn’t change that much over the year. For example, since 2020, the quarterly production of gold has ranged between 1 and 1.25 tons.
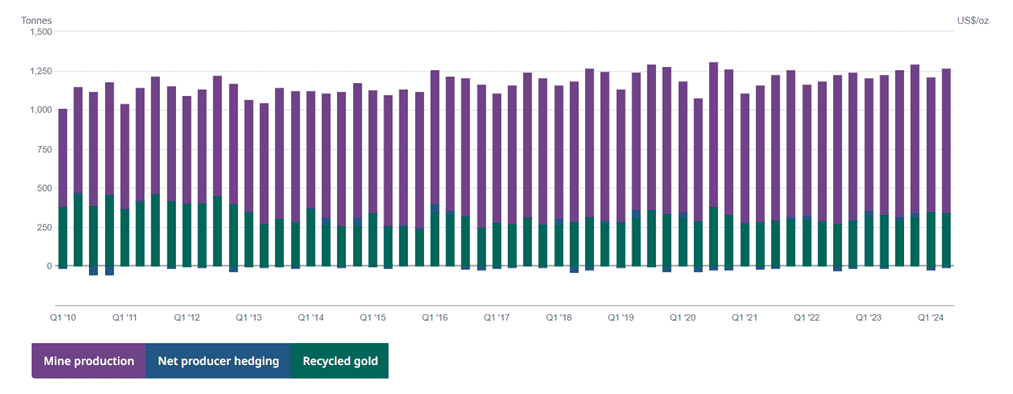
Source: World Gold Council
Total demand has also been moving within a horizontal range during the same period. You can see that demand from central banks has increased, which has had a positive effect on the metal’s price recently.
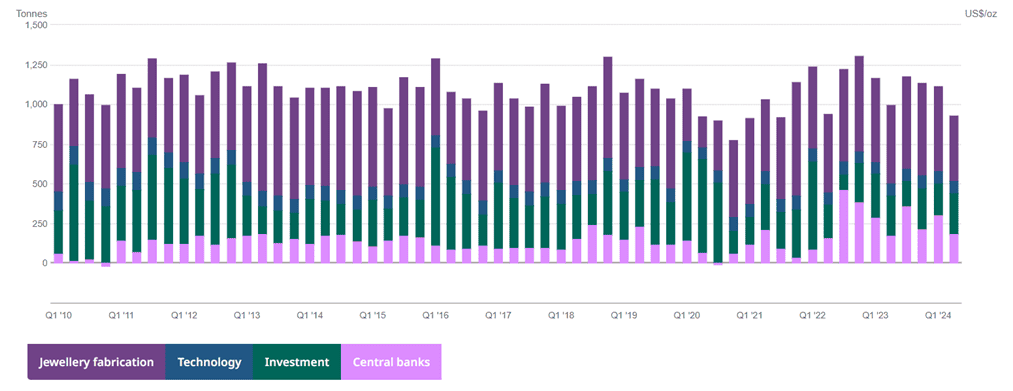
Market Sentiment
Since gold’s supply/demand dynamics are relatively stable, market sentiment is a more significant factor affecting the metal’s price. Sentiment refers to how gold is perceived by institutional and retail investors as well as the general public. If the market is pessimistic about the broader economy, this may turn investors to gold in an effort to preserve value, and that’s a driving factor for the metal.
Notice how the last two major crises – the financial meltdown in 2008 and the COVID-related crisis in 2020 – resulted in the gold price reaching new all-time highs.
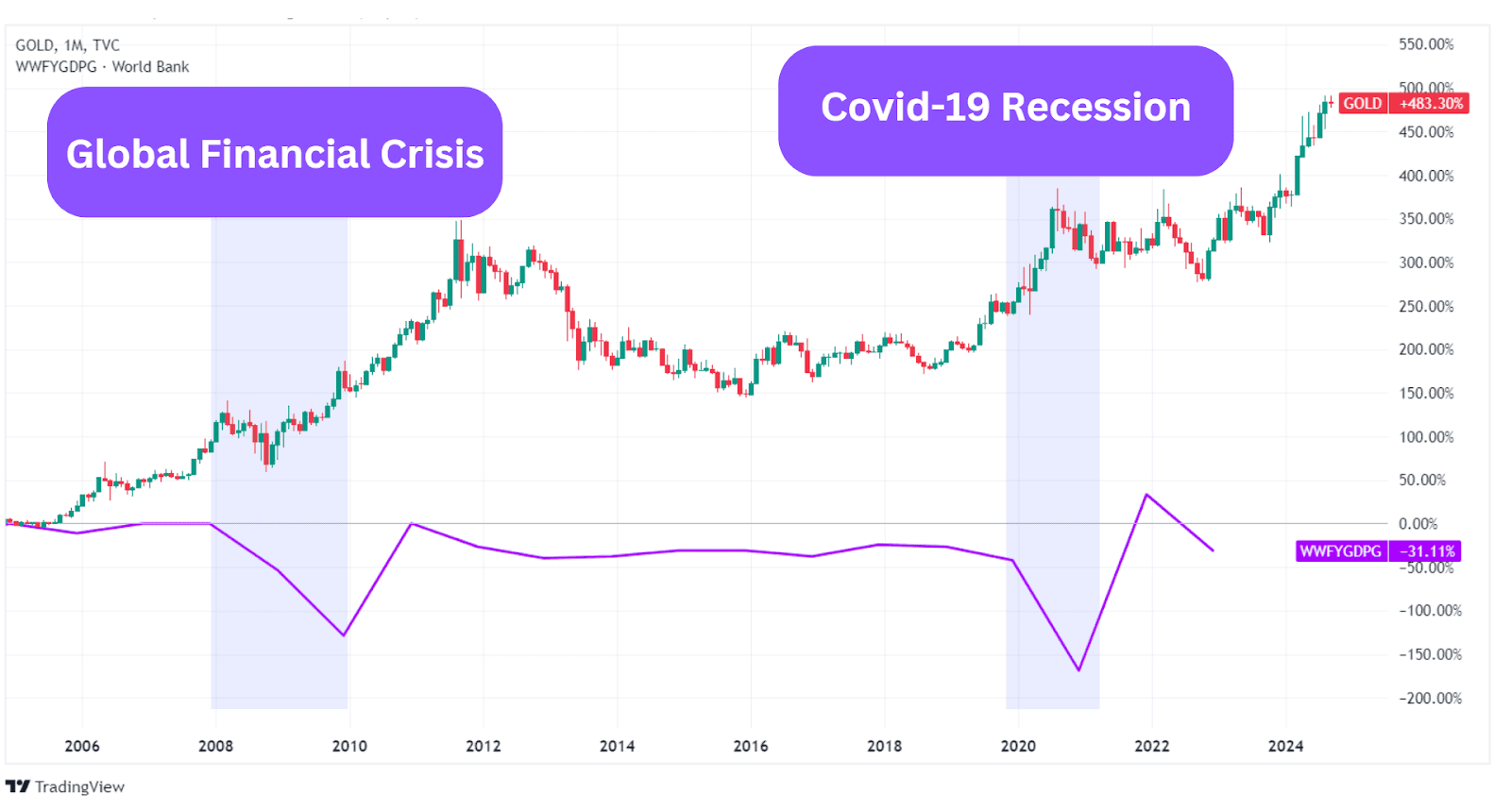
Economic Conditions
As mentioned, economic conditions have a say in the market sentiment for gold. Economic uncertainty and financial crises are closely tied to market sentiment, which can lead to increased volatility in the price of gold.
If you look at the chart above again, you can see that the gold price continued to increase for many months even as the global economy recovered from the 2008 crisis. This is because market sentiment for gold was driven by the Eurozone debt crisis in 2011.
During such times, gold acts as a safe haven for investors, helping them stabilise portfolios. In times of economic recession, riskier investments such as equities are often abandoned in favour of safer alternatives like the yellow metal.
Geopolitical Situation
Another factor impacting gold’s market sentiment is the political and geopolitical situation, as it may have a direct influence on the regional or global economy.
As a rule, global instability drives investors to gold.
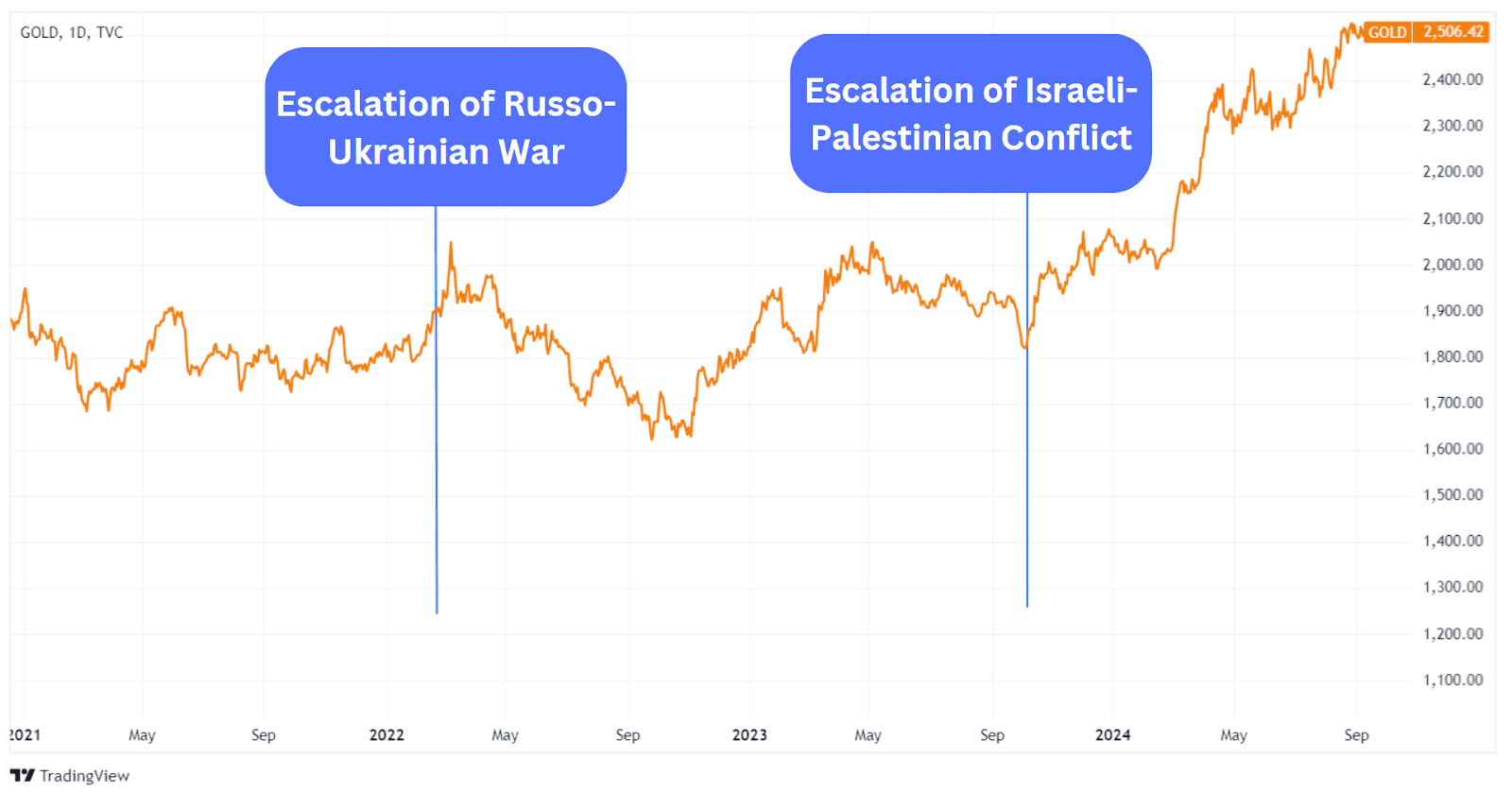
In Q3 2024, gold reached a new record high amid ongoing tensions between the West and the East, with wars in Ukraine and Gaza intensifying.
Currency Movements
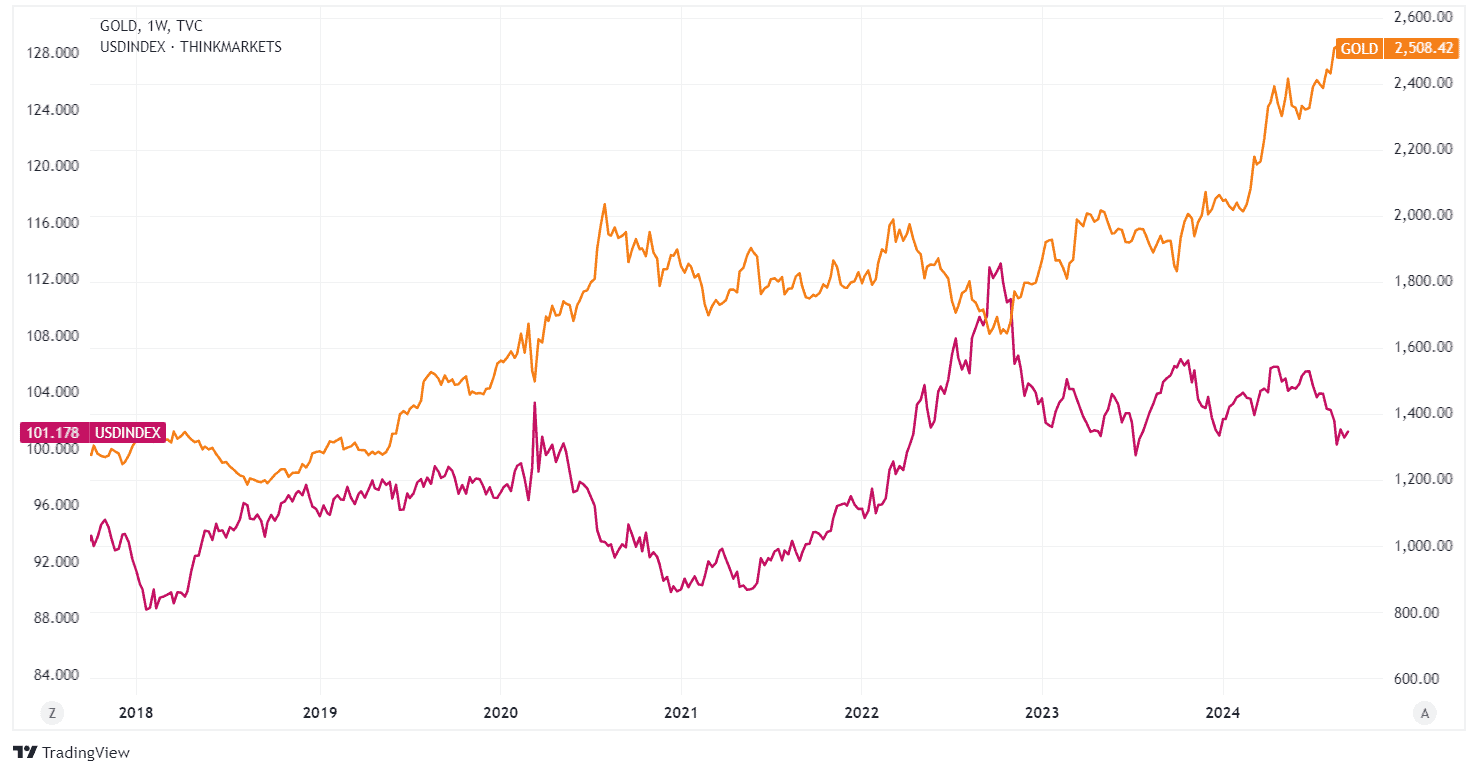
Gold is predominantly traded in USD, meaning the value of the US dollar plays a significant role in determining gold prices. There is often an inverse relationship between the two: when the US dollar strengthens, gold prices tend to decline, and vice versa.
This chart shows the relationship between the gold price and the USD Index, which measures the greenback’s value against a basket of major currencies.
Inflation and Deflation
When national currencies become unstable due to high inflation or deflation, gold is preferred for its safe-haven status, driving up demand and, consequently, its price.
For example, the COVID lockdowns prompted central banks to unlock free money with zero interest rates, which eventually sent inflation levels to the highest in 40 years. This has been a driving factor for the metal, which continued its growth.
When inflation rates are low or stable, gold tends to lose some of its appeal, often leading to lower prices.
Interest Rates
Although not directly linked, interest rates can influence gold prices.
Raising interest rates boosts returns on savings accounts, making them more attractive than gold investments, which don’t yield interest. As a result, gold prices often decline when interest rates go up.
However, there are several types of interest rates out in the market, so which interest rate should you follow?
Real interest rates have a particularly strong impact on gold because they factor in inflation. Real interest rates are calculated by subtracting inflation from the nominal interest rates. (A nominal interest rate is the headline interest rate figures).
When inflation is high relative to the nominal rate, then real interest rates tend to be low or even negative. This makes gold an attractive option as a hedge. Conversely, when inflation is low relative to nominal rates, then real interest rates rise, making interest-bearing assets more appealing, thus negatively impacting gold’s attractiveness.
You can observe the inverse correlation on this 3-year chart:
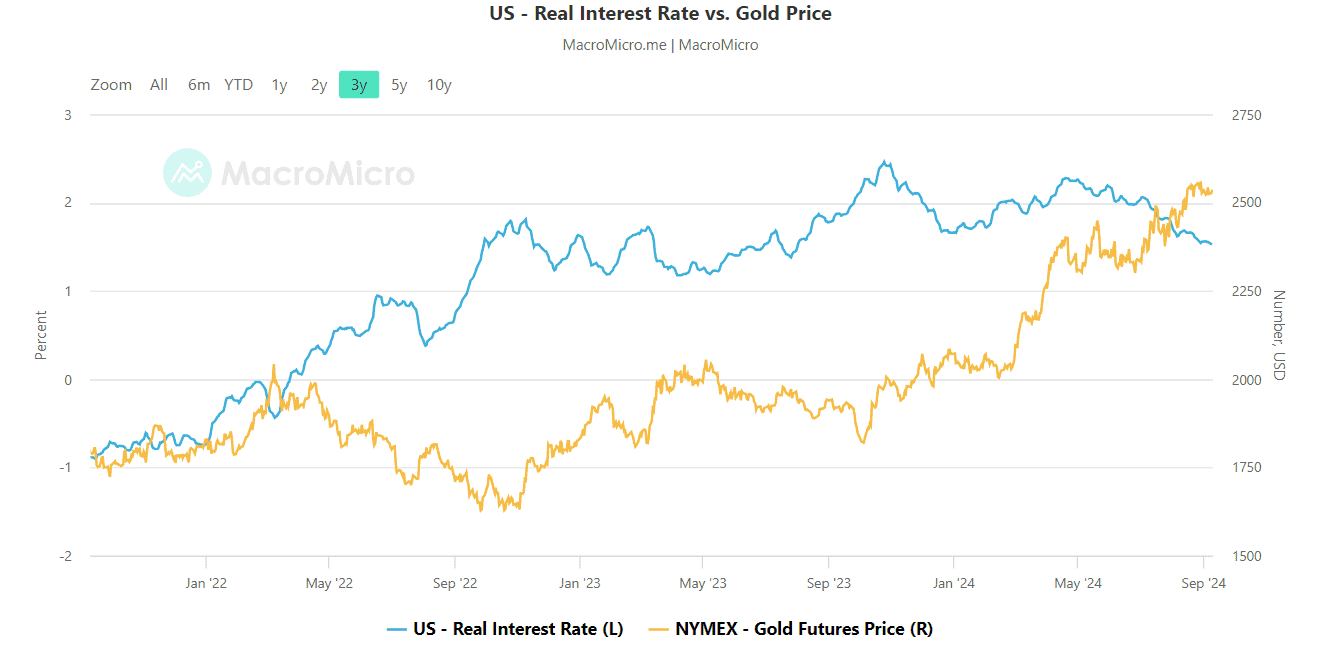
Source: Macromicro
Why Trade Gold CFDs?
While there are many ways to gain exposure to gold such as gold stocks, or gold futures, many active traders prefer gold CFDs due to their flexibility and convenience. Here are the main reasons why gold CFDs are better:
- Accessibility
Buying physical gold involves a more complex process, and the cost is high. For example, a gold bar weighing 1 kg is priced at over $80,000. In contrast, setting up a CFD trading account is easy. Plus, you can trade gold in much smaller increments of 1 troy ounce or 0.01 lot trade size. Gold CFDs provide an affordable and convenient way to access the gold market with a few clicks. - Liquidity
Gold CFDs benefit from high liquidity due to the increased interest from investors. The daily trading volume of gold is over $160 billion, surpassing US Treasury Bills and popular forex pairs like EUR/GBP.
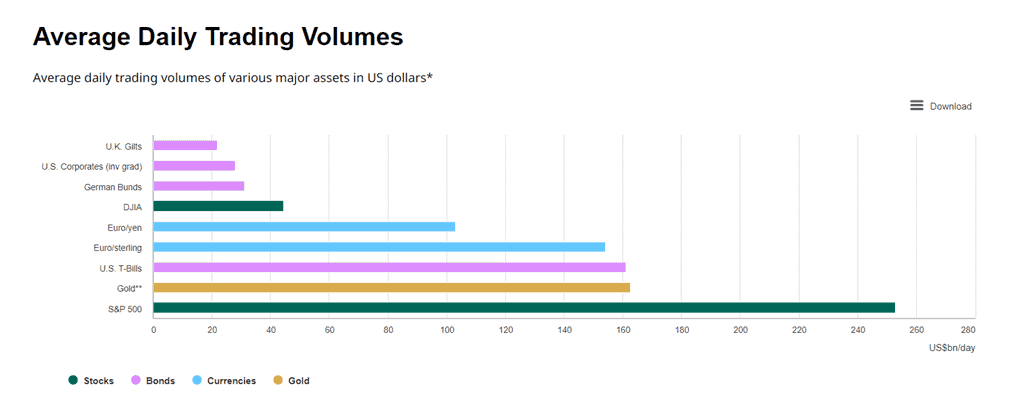
Source: World Gold Council
For gold CFDs, this means lower trading costs and commissions compared to less popular assets.
- The Ability to Go Long or Short
Unlike purchasing the physical metal, gold CFDs allow traders to profit in both rising and falling markets. You can ‘go long’ if you expect the gold price is about to rise or ‘go short’ if you anticipate a price decline. Some CFD brokers offer the one-click trading feature, allowing users to open a long or short position with a single click. - Leverage
CFDs are leveraged products, requiring traders to make a good faith deposit for only a fraction of the total contract value. For instance, with 10:1 leverage (where its geographically available), you can open a $10,000 position by depositing just $1,000. - No Contract Expiration
Gold CFDs don’t have a fixed expiration date like futures contracts. You can hold a position until you reach your desired profit margin. However, if the price moves against you, the broker may automatically close the position when the floating losses use up the available and unused margin in the account. Also, note that brokers incorporate an overnight finance charge as the funds to open the position are borrowed from the broker. - Diversification
Gold CFDs are provided by brokers that also offer exposure to forex pairs and equities, making it easy to build a diversified portfolio. Gold often behaves differently from traditional asset classes like stocks, and it can serve as a hedge against market volatility.
Gold CFDs Example
Let’s say that you want to open a long position on gold. In our example, gold’s current sell/buy price is $2,450.00/2,450.50. One gold CFD typically represents 100 troy ounces of gold with most brokers.
You decide to buy one-tenth of a CFD (0.1) worth a total of $24,505 with 50:1 leverage. (Please note, the leverage amounts will differ based on your geographic location. Check with Alchemy what your leverage would be based on your residence.) Therefore, the broker requires you to have a 2% margin, and you have to make a margin deposit of $490.10 of your own funds for the long position.
In this scenario, the price of gold increases to $2,500.50/$2,501.00. If you want to close the contract and take profits, you would sell at $2,500.50. The total value of your position has increased from $24,505 to $25,005, resulting in a profit of $500. While this represents only a 2% increase in the value of the position, your account value has increased $500 while only $490.10 of margin was required. Once the position is closed, the margin deposit of $490.10 is returned to your account and those funds are available to open other trades.

(hypothetical example used for illustrative purposes of how a trade works)
If the gold cfd prices had moved against you, a 2% decline would mean losing $500. Therefore, if your available and unused margin was greater than $500 when the trade was opened, then that $500 loss would reduce that unused margin. If you had less than $500 of unused margin when the trade was opened, then you would have received a margin call unless you deposited more funds.
In a margin call, some or all of your good faith deposit is used to cover any losses and the trade is automatically closed. If there is any of the deposit left over, then it is returned to your account as unused and available margin.
Trading on margin and using leverage is risky. To prevent significant losses, it’s recommended that risk management techniques, such as stop-loss orders, be implemented to close out the positions before the losses become too great.
Gold CFDs Trading Strategies
1. XAU/USD vs XAU/EUR
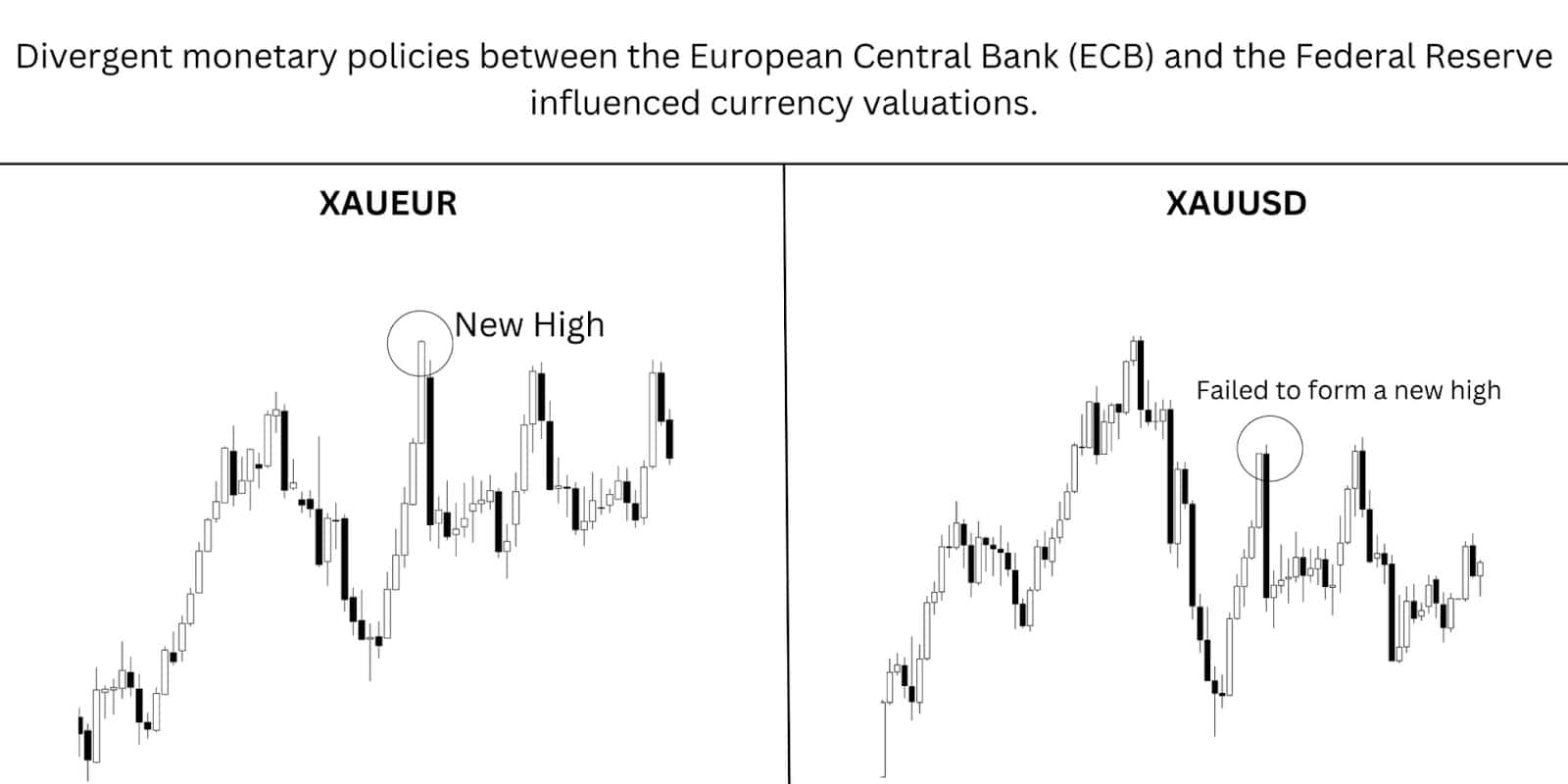
This strategy involves trading gold against two major currencies: the US Dollar (USD) and the Euro (EUR). Both pairs, XAU/USD and XAU/EUR, are popular among gold CFD traders, offering unique opportunities based on currency movements and macroeconomic factors.
Key Considerations:
- Correlation Differences: XAU/USD often reacts to US economic data, Federal Reserve policies, and USD strength or weakness. Meanwhile, XAU/EUR may be influenced by European Central Bank policies, Eurozone economic conditions, and geopolitical risks in Europe.
- Hedging Opportunities: If one pair moves unfavourably, the other may counterbalance the loss due to differing market dynamics, offering a natural hedge.
- Currency Volatility: Monitoring the USD Index (DXY) and EUR/USD exchange rate can provide valuable insights for trading these pairs effectively.
Example:
- If the USD strengthens due to positive US economic data, XAU/USD might fall while XAU/EUR remains stable or rises, creating opportunities to exploit the price divergence.
2. Day Trading
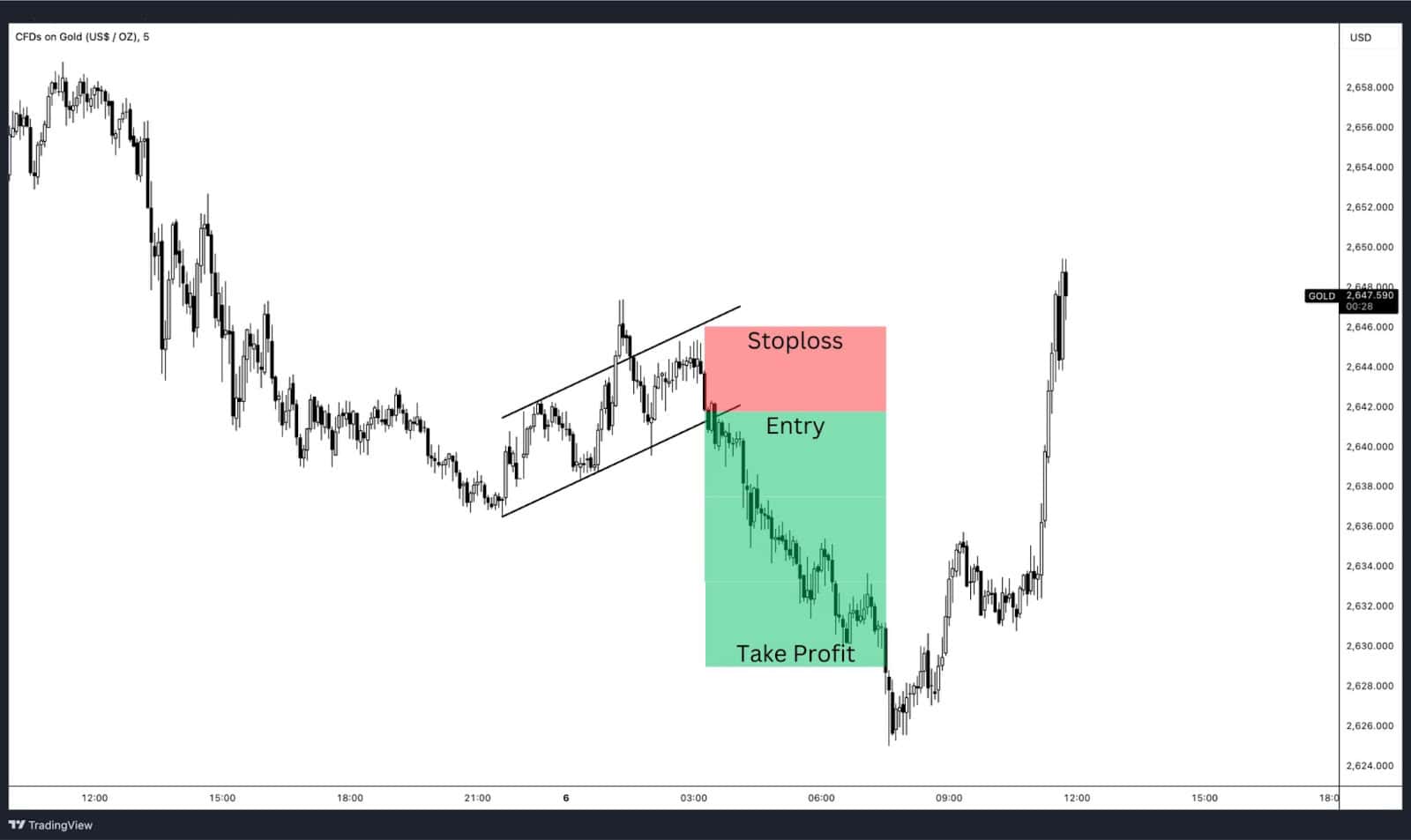
Day trading gold CFDs is a short-term strategy where traders open and close positions within a single trading session. The goal is to profit from intraday price movements driven by market volatility.
Key Features:
- Timeframes: Popular timeframes for day trading include 5-minute, 15-minute, and 1-hour charts.
- News Impact: Economic data releases, such as Non-Farm Payrolls or inflation reports, can cause significant gold price swings, presenting opportunities for quick gains.
Example:
- A trader identifies a breakout from a bearish flag pattern on a 5-minute chart and enters a short position. The trade is closed when the price hits a support level.
3. Swing Trading
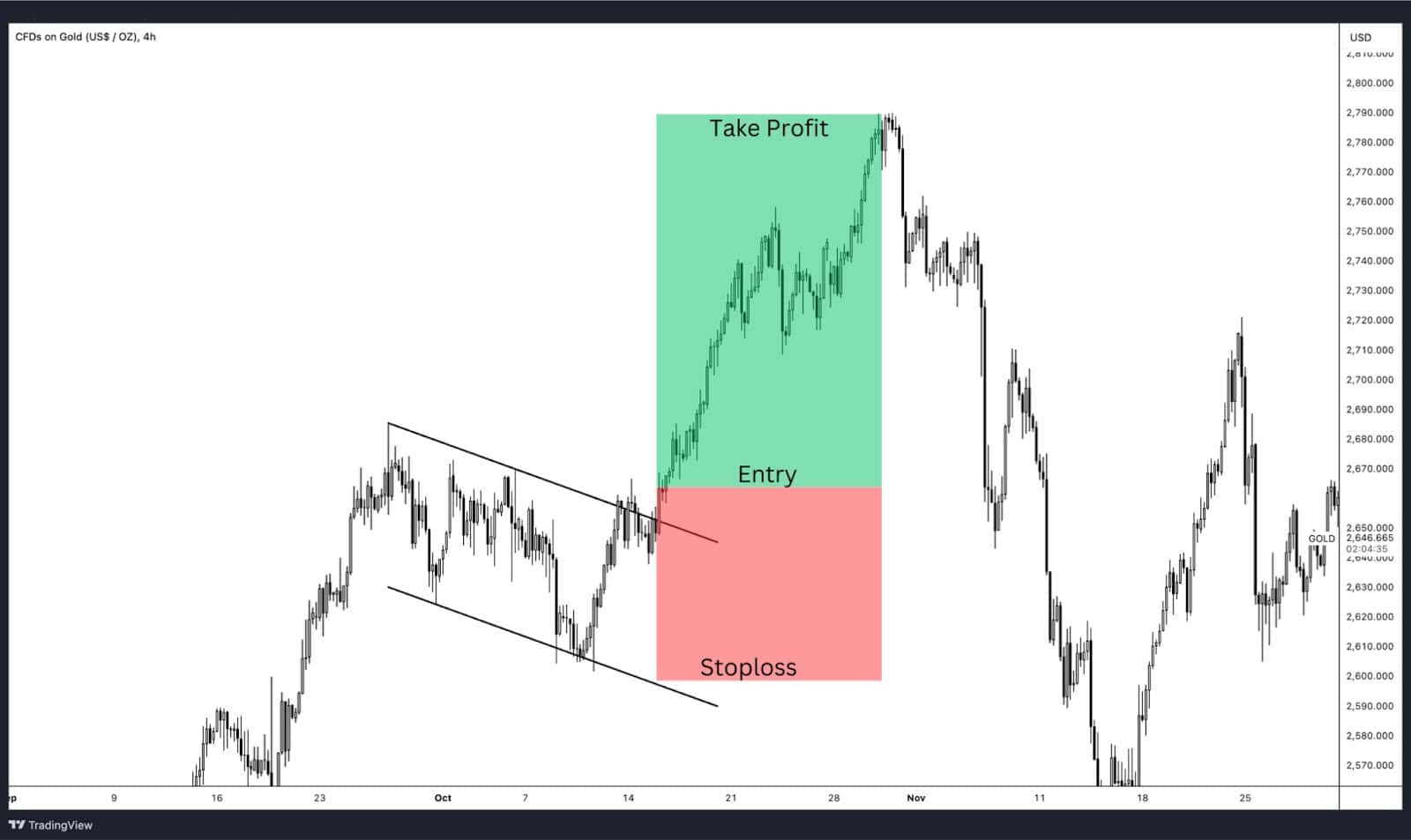
Swing trading involves holding positions for several days to weeks, aiming to capitalize on medium-term price trends.
Key Features:
- Trend Analysis: Swing traders use daily or 4-hour charts to identify bullish or bearish trends. They rely on tools like Fibonacci retracements, chart patterns and trendlines.
- Risk Management: Stop-loss and take-profit orders are crucial to manage risks, given the longer holding periods.
- Fundamental Analysis: Gold prices are influenced by factors such as inflation rates, central bank policies, and geopolitical tensions, which swing traders incorporate into their strategies.
Example:
- A trader enters a long position during an upward trend, anticipating further appreciation based on strong demand for gold. The position is held until a resistance is formed.
4. Scalping
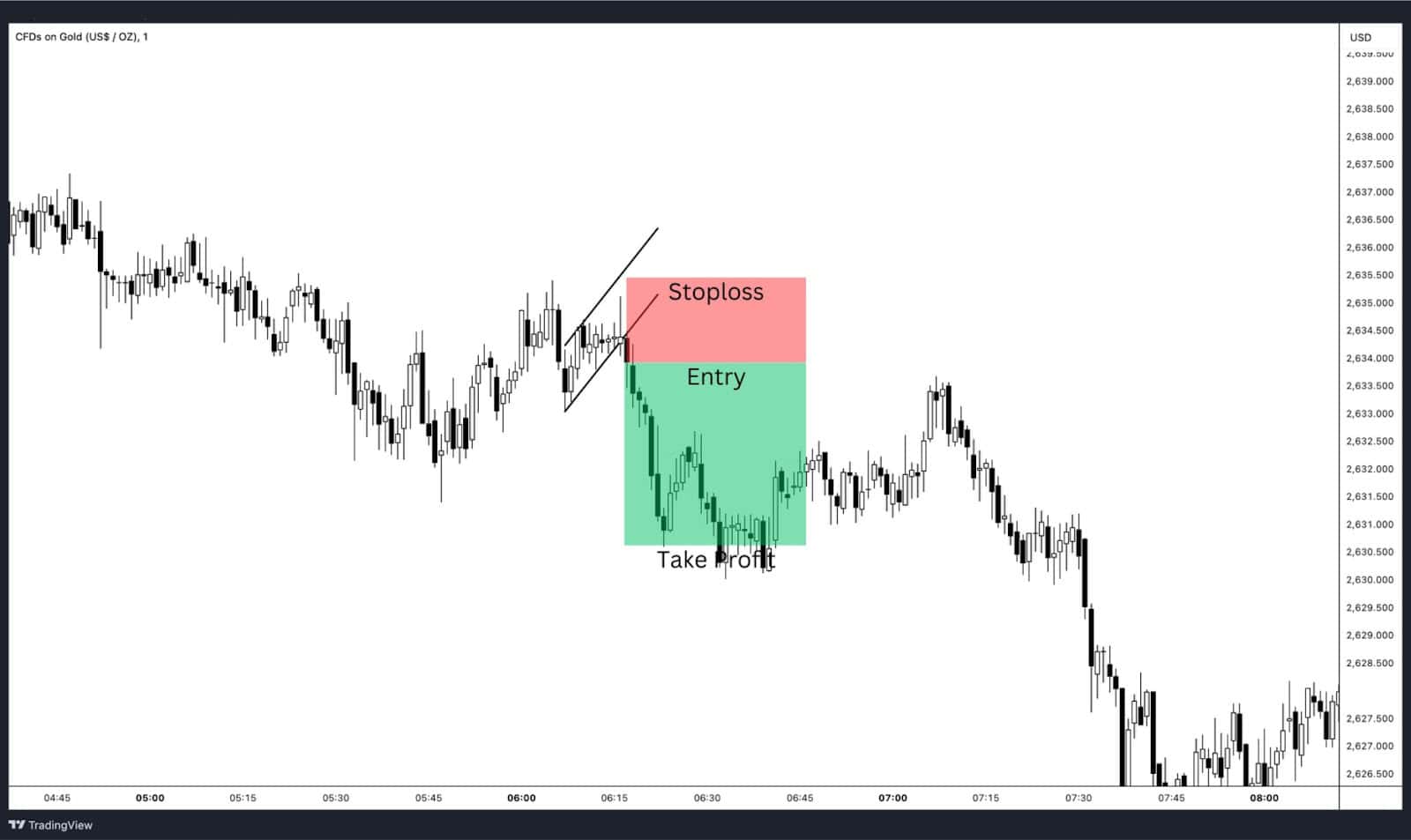
Scalping is a high-frequency strategy that involves executing multiple trades within minutes or hours to profit from small price movements.
Key Features:
- High Liquidity: Gold CFDs’ high trading volume ensures tight spreads, making them ideal for scalping.
- Low Timeframes: Scalpers use 1-minute or 5-minute charts to find quick opportunities.
- Small Targets: Trades aim for small price increments, often exiting positions after a $1–$2 movement in gold prices.
- Leverage Use: Scalping often involves higher leverage to amplify profits, although this also increases risks.
Example:
- A scalper notices a price consolidation and anticipates a breakout. They quickly open a position and close it as soon as the price moves in their favor, even by a smaller margin.
Advantages of Gold CFDs
- Short selling – unlike buying gold or gold ETFs, CFDs allow traders the ability to profit from gold price declines during bearish markets.
- Volatility – while gold is not as volatile as many stocks or cryptocurrencies, it still shows more significant fluctuations compared to major forex pairs like EUR/USD, offering more opportunities for active trading.
- Leverage – traders can use leverage to multiply the outcomes of their trades with gold CFDs. This means less capital is required to run their strategy as traders can open large positions with only a fraction of the trade’s size needed for margin. Leverage does amplify losses as well as gains so it needs to be carefully implemented, if at all.
- Convenience – gold CFDs are more convenient than buying physical gold, as traders don’t have to engage in complex trading processes and don’t have to think about transportation and storage.
- Regulated environment – reputable CFD brokers, such as Alchemy, are licensed and regulated by some of the most prominent regulators in the world. This means you are depositing and trading with a reputable broker.
- Advanced terminals & tools – Alchemy offers advanced trading terminals like MT4. Additionally, you’ll find a wealth of educational and trading resources, like our analysts and Trading Central, to help you on your strategy and spot trading opportunities.
Disadvantages of Gold CFDs
- Margin trading risks – while leveraged trading is listed as an advantage, it carries a high risk of rapid losses if the price of gold moves against your position.
- CFDs are illegal in some jurisdictions – in some countries, including the US, CFD trading is prohibited due to regulatory restrictions.
- Overnight costs – some brokers may charge additional costs for holding a CFD position open overnight to finance the trade on margin. This makes the long-term trading strategy less efficient as costs eat away at holding the position open. You can find the overnight finance charges in your account’s trading terminal.
Gold CFDs vs Gold Futures
Both gold CFDs and futures enable short selling which is a joint advantage over trading physical gold.
Gold futures are derivative contracts to buy or sell the metal at a predetermined price for delivery at a specified time. However, there is a big difference between futures and CFDs. Gold futures have an expiry date, requiring traders to settle at the agreed-upon price when the contract was initiated. Those trades can be closed prior to expiry so delivery doesn’t take place. However, this means the trader has to actively monitor the expiry date of the contract.
When trading gold CFDs, there is no contract expiry. Gold CFD traders can hold the trade open for any length of time without having to worry about delivery.
Additionally, you can trade gold priced in Euros with a XAU/EUR CFD. This means that if gold and Euro are trending in opposite directions, then you can make one simple trade on XAU/EUR without having to open two futures contracts on gold futures and Euro futures.
Gold CFDs vs Gold ETFs
A more direct exposure to gold is provided by gold ETFs, which are funds backed by physical gold. The ETFs can be traded in the form of shares via traditional stock exchanges, such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE). The experience is quite similar to trading stocks.
The largest gold ETFs are SPDR Gold Trust (NYSEARCA: GLD), issued by State Street Global Advisors, with total assets under management (AUM) of nearly $69 billion, and iShares Gold Trust (NYSEARCA: IAU) offered by BlackRock, with $29 billion AUM. You can check the chart below to see how close these two ETFs follow the price of gold.
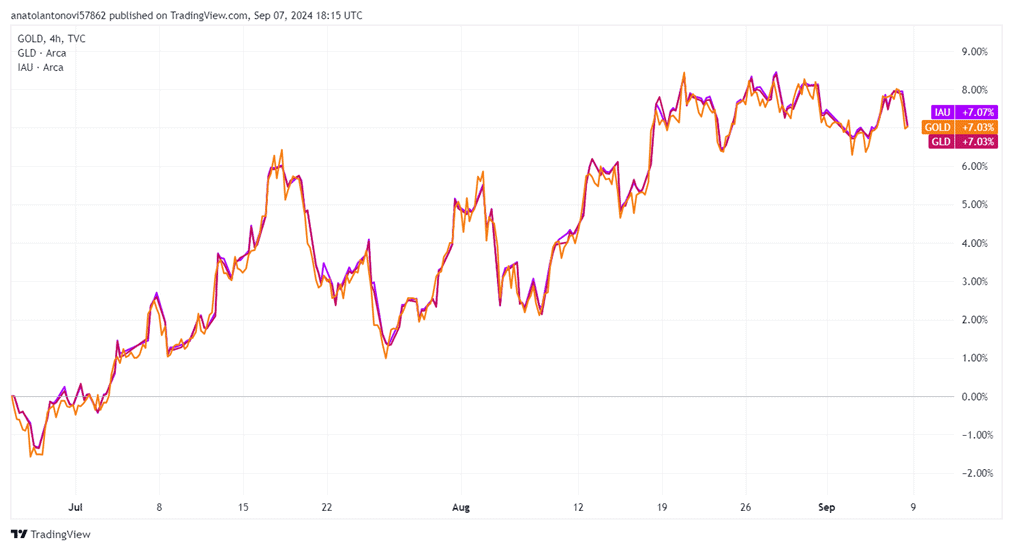
The challenge with ETFs is that they are more complicated to short unless you have a margin account. To counteract that, institutions have created inverse ETFs that run inverse to the price of gold. In an inverse gold ETF, if the gold price drops, then the inverse ETF price moves higher. However, the simplicity and flexibility to go long or short in a gold CFD makes it easier to manage rather than researching an ETF to go long and another ETF to go short.
There are some ETFs out there that are leveraged, but the leverage may only be 2x or 3x the price of gold. Over longer holding periods, those leveraged ETFs are less likely to follow the price of gold and more likely to underperform due to their recalibration. Therefore, if you are looking for leverage in a gold position, gold CFDs offer the leverage, simplicity, and pure price performance versus leveraged ETFs.
The advantage to the non-levered Gold ETF is if you plan to hold the position for a longer period of time. The CFD finance charges would eat away at your profits while the ETF fees are much smaller making long-term holdings more efficient.
Gold CFDs vs Gold Miner Stocks
Gold CFDs show a significant correlation to gold miner stocks, and many prefer the latter.
Stocks represent ownership so gold miner stocks means a trader is owning a portion of the company. For more active traders, these gold miner stocks may be more volatile and some companies pay quarterly dividends.
A gold CFD trade does not imply ownership and your position simply mirrors the price of gold. Though you can quickly get into and out of long and short positions,with a gold CFD, a gold miner stock will be a long only position.
A big challenge with gold miner stocks is that they are equities. So, if the equity market declines, gold mining stocks tend to decline with it regardless of what the price of gold is doing. As a result, there are times when gold would outperform a basket of mining stocks, then there are other times with the gold mining stocks might outperform gold.
Over the past five years, gold has outperformed the world’s biggest gold mining companies by market cap, as you can see in the chart below (note that the purple line represents Barrick Gold Corporation, whose ticker is also GOLD).
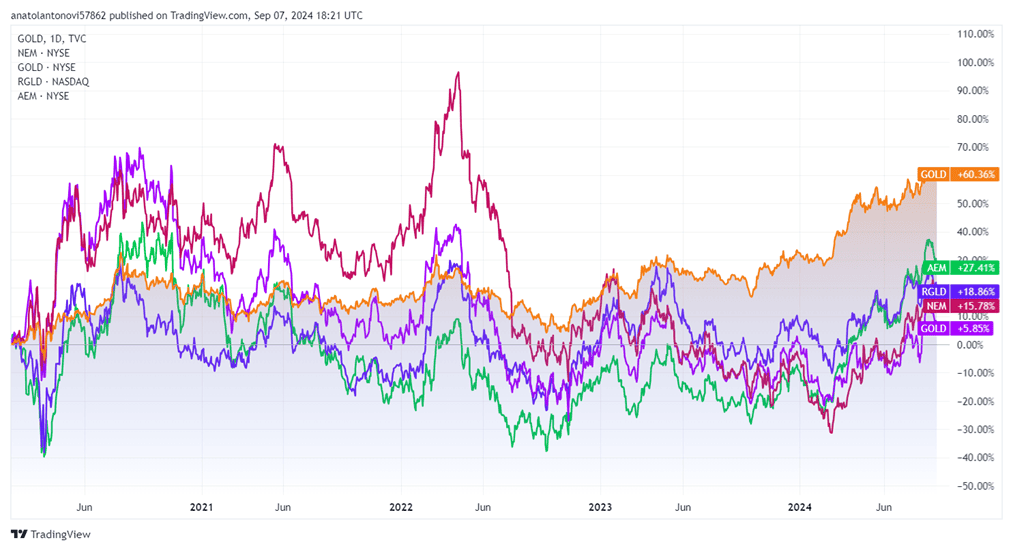
Gold CFD vs Bitcoin CFD
Bitcoin, the largest cryptocurrency by market cap, is often compared to gold and has been frequently called “Digital Gold”. Although fundamentally different – gold is a physical metal while bitcoin is a virtual currency – both assets are regarded as a hedge against money printing inflation.
With the introduction of Bitcoin ETFs at the beginning of 2024, the one-year correlation between gold and bitcoin increased to a record high in June 2024. However, gold has historically shown cyclical fluctuations of moving into and out of correlation with bitcoin.
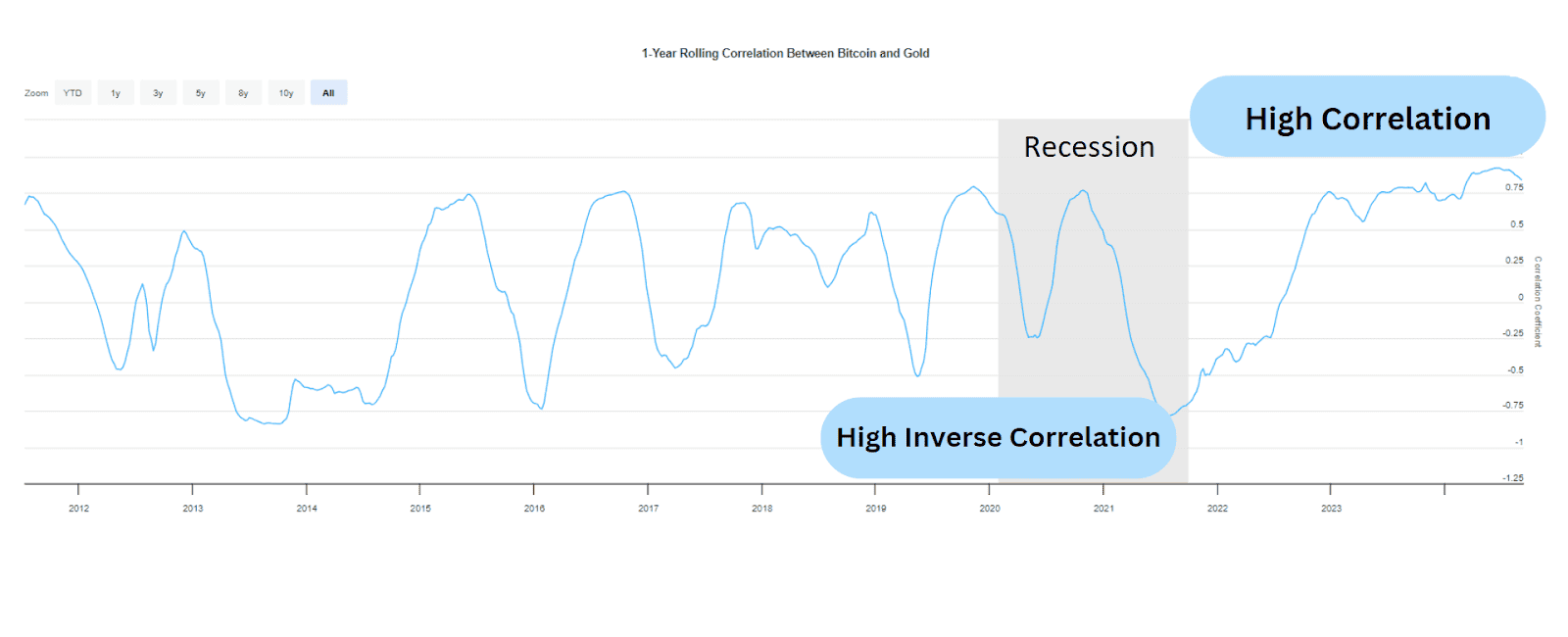
Although known for their scarcity, gold is very different from bitcoin. Trading Bitcoin CFDs exposes traders to increased volatility that may defy traditional technical analysis and catch investors off guard.
Gold is a lower-risk and lower-return investment, while BTC has been a high-risk and high-return investment.
Gold CFD vs Silver CFD
Both gold and silver are great investments to hedge against inflation, but gold is regarded as a stronger safe haven due to its stability and long-term store of value. Meanwhile, silver is often dubbed ‘poor man’s gold’ since it’s more affordable. Many retail traders prefer silver because of its lower cost and higher volatility.
Silver’s higher volatility is mainly driven by its industrial use. As per the World Silver Survey, about 50% of silver is used in heavy industry and technology, which makes silver more sensitive to economic changes compared to gold. The yellow metal is mainly used for jewellery and investment purposes.
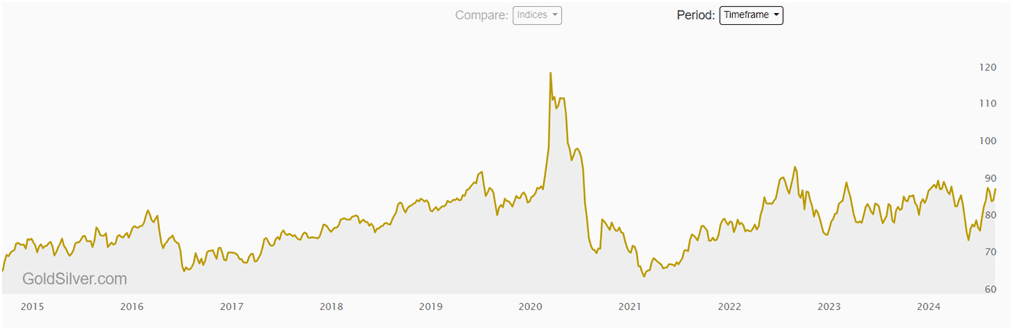
The gold/silver ratio, which expresses the number of silver ounces it takes to equal one ounce of gold, can help traders assess potential opportunities. Historically, when the ratio is high, some traders see silver as undervalued compared to gold, and vice versa. Currently, with the ratio at 88, it is considered to be on the higher end.
Gold Trading Platform for Alchemy Markets
At Alchemy Markets, our gold trading platform is designed to provide traders with seamless access to global gold markets with competitive pricing, deep liquidity, and advanced trading tools. Whether you’re a short-term trader looking to capitalize on market volatility or a long-term investor seeking to hedge against economic uncertainty, our platform offers the flexibility and efficiency you need. With real-time market data, tight spreads, and fast execution, Alchemy Markets ensures you can trade gold CFDs with confidence.
Our gold trading platform supports multiple order types, technical analysis tools, and risk management features to help traders make informed decisions. You can access gold markets 24/5 across desktop, web, and mobile devices, ensuring you’re never out of touch with price movements. Additionally, our platform integrates seamlessly with MetaTrader 4 (MT4) and MetaTrader 5 (MT5), allowing you to execute trades with professional-grade features. Whether you’re trading XAU/USD or exploring gold as part of a diversified portfolio, Alchemy Markets delivers a powerful and user-friendly trading experience.
How to Trade Gold CFDs
Beginners can start trading gold CFDs by following these simple steps:
- Open a trading account and deposit funds – you can register with Alchemy by clicking on “Open Account” on top of the homepage and sharing personal data, such as name, email, and phone number. You will be required to set up a strong password, choose a currency, and agree with the conditions.
- Once registered, make sure to pass the KYC verification by sharing the photos of your ID documents and deposit funds via wire transfer, credit/debit card, or Skrill.
- Open MT4 – when you’re set up with Alchemy, you can go to the MT4 terminal. Choose the CFD product you prefer, such as XAU/USD, XAU/EUR, or maybe gold miner stocks.
- Analyze markets & prepare strategy – you must have a trading strategy and identify trading opportunities that fit your strategy logic. There are many different strategies, but try to use the most basic technical indicators to start.
- Open a position – you can open a position on MT4 with or without using leverage. Risk management tools like stop-loss orders should be used to minimise potential losses.
- Monitor your trade – keep an eye on your trade while it’s open using technical indicators. With time, you’ll learn to read the market.
- Close your position – if the trade meets your price target, it’s time to close the position and secure your profits. If the stop-loss is triggered, don’t be disappointed – your next trade may be profitable. It’s best to start by training on a demo account first.
FAQ
What are the best timeframes to trade gold CFDs?
The best timeframes for trading Gold CFDs depend on your strategy. For short-term traders, intraday timeframes like M15 or H1 are popular, while swing traders often use H4 or daily or weekly charts for broader trends.
Can I trade gold with Metatrader 4 and Metatrader 5?
Yes, both MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5 support Gold CFD trading, offering advanced charting tools, indicators, and automated strategies. However, it depends on the broker. Alchemy Markets currently supports MT4, MT5, and DX Trade platforms.
How much capital do you need to trade gold CFD?
The amount of capital needed to trade gold CFDs depends on your strategy and how much risk-based capital you have available. You can start with as little as $100. Make sure to always trade with funds you can afford to lose.
What is the origin of gold trading?
Gold trading dates back thousands of years. It was initially as a currency and later as a store of value and an investment asset.
Why is gold a safe haven asset?
Gold is considered a safe-haven asset because it tends to preserve value or increase in price during times of economic uncertainty or geopolitical instability, being a good hedge against inflation. Additionally, gold has survived thousands of years while other currencies have come and gone.
Is it worth it to trade gold CFDs?
Trading Gold CFDs can be worth it for those looking to capitalize on price movements without owning physical gold, offering flexibility and leverage, but it carries risks like any financial product.
Is gold a CFD in forex?
In forex trading, currencies are traded in pairs, and gold is paired with a currency like the USD (XAU/USD) or EUR (XAU/EUR) in CFD trading. This allows traders to speculate on the price of gold without owning it, making gold CFDs a part of forex trading.
What is the size of a gold CFD contract?
A standard Gold CFD contract typically represents 100 troy ounces of gold, but this may vary depending on the broker and platform used. Some brokers offer mini-contracts of 10 ounces.







