
- Opening Bell
- September 19, 2024
- 6 min read
Fed Cuts Deep, BoE Stays Cool
Federal Reserve Rate Cut: A Bold Move
The Federal Reserve’s decision to cut its federal funds rate by an unexpected 0.5 percentage points has sparked significant attention across financial markets. The Fed now targets a range of 4.75% to 5%, signalling a cautious but more accommodative stance in its fight against inflation.
Recent data indicates that while job gains have slowed and unemployment has slightly risen, inflation is inching closer to the Fed’s 2% goal. With progress being made, the central bank felt confident in easing monetary policy—but they’ve been careful to stress that this is not the start of a domino effect of rate cuts. Instead, each decision will be taken on a meeting-by-meeting basis, considering the evolving economic conditions.
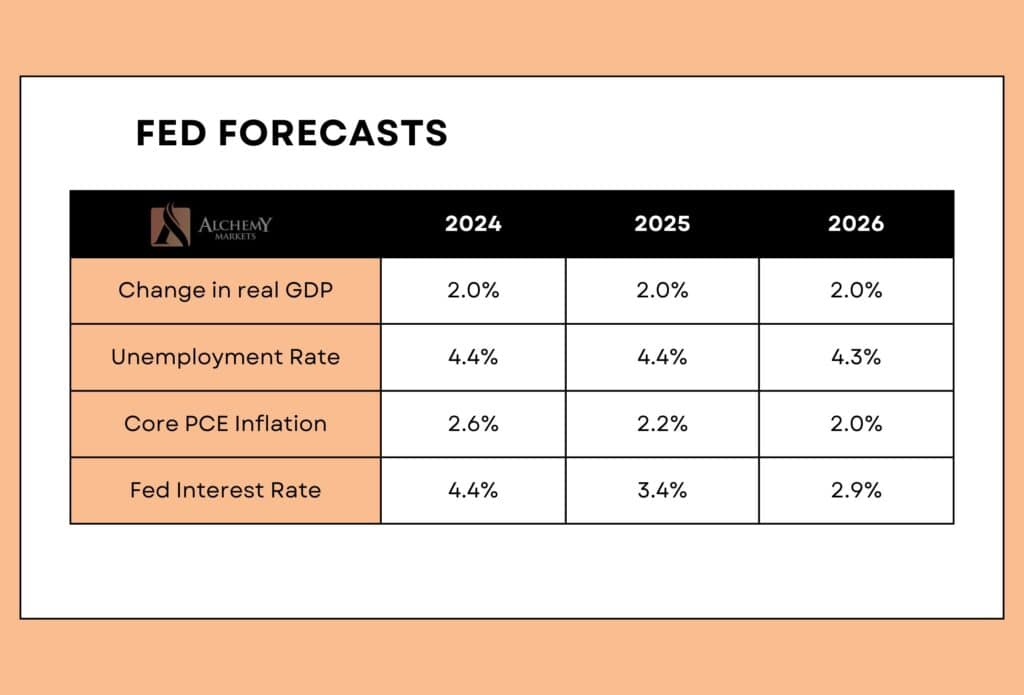
Key Highlights from the Fed Decision:
- Rate Cut: A 0.5% reduction in the federal funds rate, now targeting 4.75%–5%.
- Inflation Progress: Movement towards the 2% target continues, though inflation remains somewhat elevated.
- Employment Outlook: Job growth has slowed, but unemployment remains low.
- Monitoring Risks: The Fed remains vigilant, ready to adjust its stance if risks emerge that threaten economic stability.
Despite this relatively dovish move, the Fed reassured the market that it remains committed to supporting maximum employment and returning inflation to its long-term target. Their next steps will be guided by economic data and financial developments, keeping flexibility in their approach.
Market Reaction: Surprising Rally and Dollar Weakness
The larger-than-expected rate cut, though unexpected, was not seen as a panic move. This could create positive momentum in the stock market, especially among sectors like real estate and technology that benefit from lower borrowing costs.
S&P 500 (SPX)
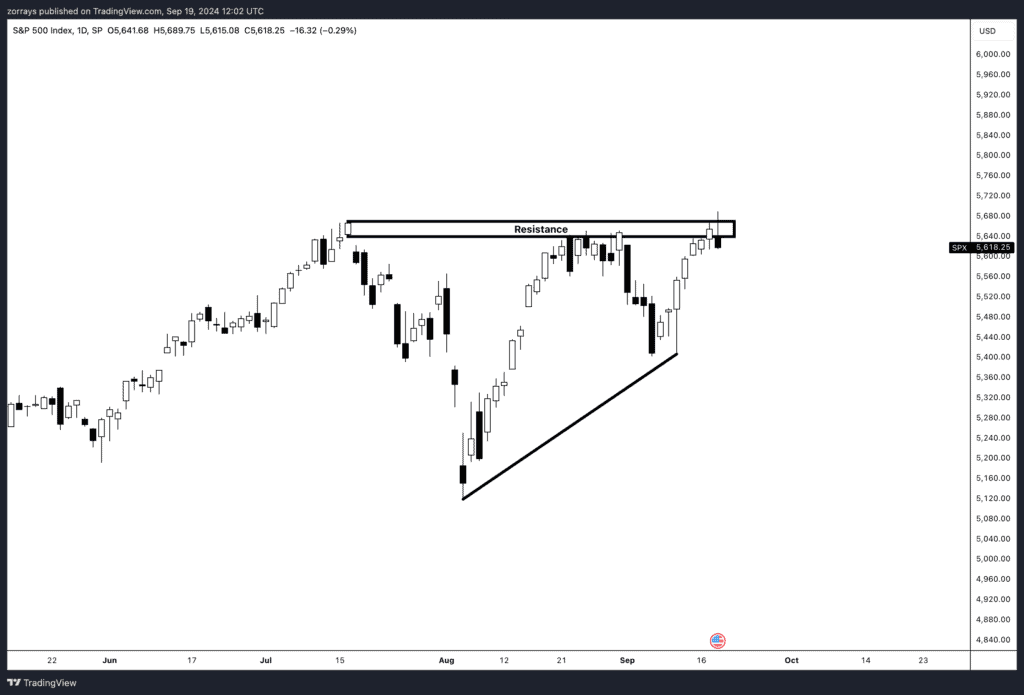
The market is currently showing signs of anticipation as it waits for the S&P 500 Index (SPX) to break to the upside from the ascending triangle formation. This technical pattern is often seen as a bullish signal, indicating that if price can successfully break above the defined resistance level, it may suggest a continuation of the upward trend. Traders are closely watching this area, as a breakout would likely trigger further buying interest.
Dollar Index (DXY)
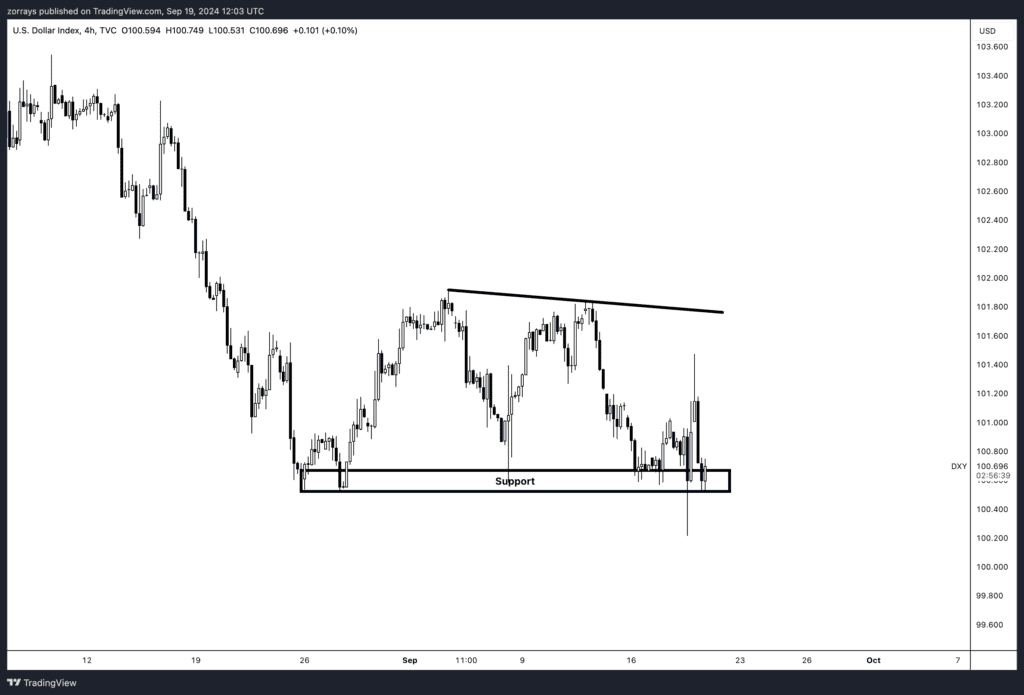
On the other hand, the U.S. Dollar Index (DXY) is forming a descending triangle, typically a bearish continuation pattern. The market sentiment around the dollar remains dovish, especially with expectations of a more accommodative monetary policy from the Federal Reserve. This dovish stance could lead to further weakness in the dollar. If the DXY breaks below the established support level, it would confirm the bearish bias, potentially leading to further declines in the dollar’s value.
Bank of England: Holding Steady Amid Inflation Pressures
In contrast to the Fed’s rate cut, the Bank of England (BoE) opted to keep its Bank Rate unchanged at 5% during its September 2024 meeting. This decision was supported by a majority of 8-1, with only one member favouring a minor cut of 0.25 percentage points. The Bank’s primary focus remains its battle against inflation, which remains stubborn despite some global improvements.
Accelerated Rate Cuts on the Horizon for the BoE
The Bank of England’s rate cuts are expected to accelerate beyond November, as inflationary pressures show signs of easing. While services inflation has been sticky due to volatile categories, the broader picture is improving, with wage growth and inflation expectations starting to cool. Employment data, though imperfect, points to a slowdown, with fewer payrolled employees and companies revising down their wage and price growth forecasts.
Given these trends, the BoE is likely to grow more confident in controlling inflation, leading to a faster pace of cuts. We anticipate back-to-back rate reductions, with a cut in both November and December, and further cuts in 2025, potentially bringing the Bank Rate down to 3.25% by next summer.
Key Points from the BoE Decision:
- Unchanged Rate: The BoE held its Bank Rate at 5%, with only one dissenting vote for a cut.
- Quantitative Tightening: The Bank will continue reducing its bond holdings by £100 billion over the next 12 months, bringing its stock of UK government bonds down to £558 billion.
- Inflation Target: The BoE’s goal remains clear—return inflation to 2% sustainably, though domestic inflation pressures remain a challenge, particularly with services inflation still at 5.6%.
- Wage Growth: Private sector regular earnings grew by 4.9%, indicating that wage inflation remains a concern.
The decision reflects a cautious approach to monetary policy, where the BoE recognises that while global inflation is easing, domestic price and wage pressures persist. The Bank remains committed to keeping inflation expectations anchored and will continue its policy of gradual tightening until inflation risks subside.
UK Market and Currency Outlook
With the BoE holding rates steady, the immediate reaction in the UK stock market is likely to be muted. Investors had largely anticipated this decision, given the mixed inflation data and steady global growth rates. However, there are key market takeaways that may shape future trends:
- Stock Market: Sectors sensitive to consumer spending may face pressure as higher interest rates continue to squeeze disposable income. However, stability in rates might encourage some market confidence, particularly in financial sectors.
- British Pound: With the Fed adopting a dovish tone, the pound could see some relative strength against the dollar. But, if inflation persists in the UK, further tightening from the BoE could weigh on economic growth, limiting the pound’s upside potential.
Conclusion: A Tale of Two Central Banks
Both the Federal Reserve and Bank of England are navigating uncertain economic landscapes, but their strategies diverge based on local conditions. The Fed’s unexpected rate cut signals confidence in controlling inflation while promoting growth, whereas the BoE’s more cautious approach reflects persistent inflation risks within the UK.
Market Takeaways:
- Fed: Lower interest rates could boost US stock markets and weaken the dollar.
- BoE: A steady hand could stabilise UK markets, but inflation concerns remain.
Both central banks have reiterated their commitment to taking decisions based on incoming data, meaning that future moves will be shaped by ongoing economic developments. Investors should brace for continued volatility as central banks remain cautious but adaptable.







